24-12-2025
What is a compensating capacitor? Principle of operation, function and application
Compensating capacitors are used in industrial electrical systems, especially when there are devices that need to compensate for reactive power. In the summary below, BTB Electric will help you better understand the structural characteristics, applications of compensating capacitors and how to choose the right power compensating capacitor.
What is Capacitor?
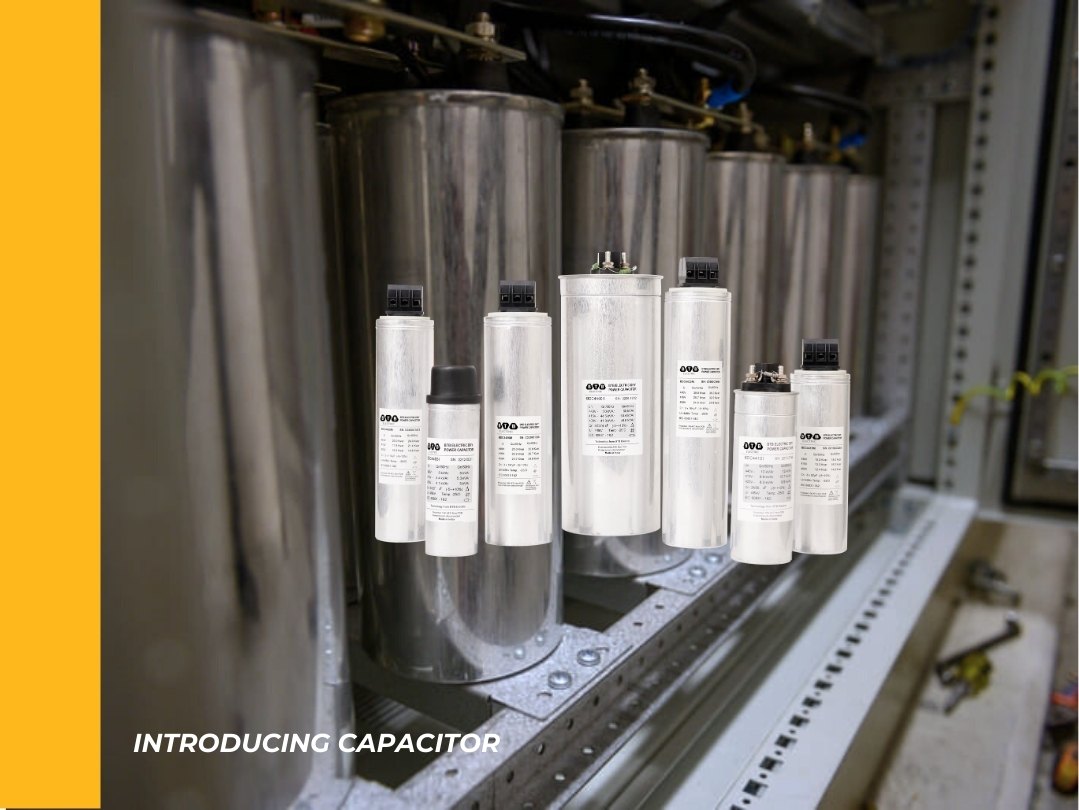
A compensating capacitor (capacitor) is a device used to compensate for the reactive power, which increases the cosφ power factor in the power system. The compensating capacitor works by charging and discharging electricity through two polar plates connected to the power supply. Similar to a single-phase compensating capacitor, a 3-phase compensating capacitor consists of three polar plates connected to the power supply, instead of two polarity plates like a single-phase compensating capacitor. Each polar plate is composed of aluminum foil, and layers of insulation are interspersed between.

The function of compensating capacitors in the power system is to ensure stability and safety when operating electrical equipment and improve the cosφ coefficient to avoid fines from the electricity side. This is also the most effective solution to reduce reactive power (unemployed power) today.
Structure of compensating capacitors
The structure of single-phase and three-phase compensating capacitors is relatively similar. The basic structure of a compensating capacitor is two or three conductors placed next to each other, separated by an insulating solvent. In fact, an electrical compensating capacitor has 2-3 polar plates at the end of which are 2-3 aluminum foils, placed close to each other and have interstitial insulation layers. This entire structure is placed in a cylindrical sealed vessel, which has an aluminum shell and a plastic shell.
Two or three pole plate ends are taken out at the top to connect to the power supply. Unlike two-phase compensating capacitors, three-phase compensating capacitors are equipped with an automatic power shut-off mechanism when overloaded to avoid capacitor explosion, this mechanism is often called explosion-proof.
The principle of operation of the compensating capacitor
Capacitors consume a small amount of energy, mainly due to internal resistance and inductance causing power loss . When electrical power is transmitted from the source to the load, there are 2 types of power produced: reactive power and applied power. The effective power is useful for the system, while the reactive power is the consumable part, not generating work, so it is necessary to use a reactive power compensator.

The working principle of the compensating capacitor is to improve the coefficient, compensate for the wasted reactive power when operating electrical equipment, thereby increasing the useful effect power.
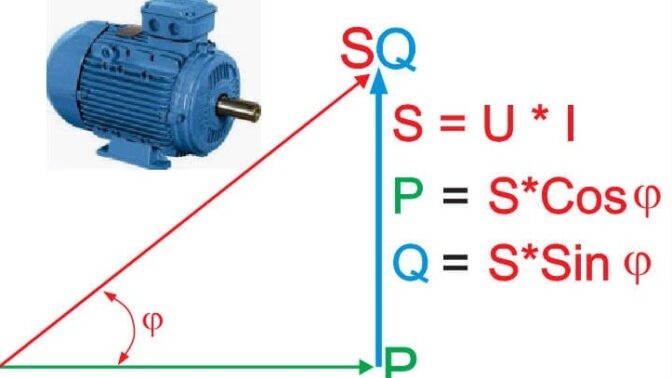
The above two types of power are closely related to each other, expressed by the following formulas:
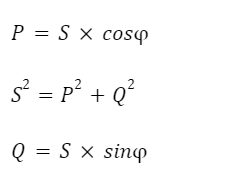
In which:
- S: Apparent Power
- P: Effective power
- Q: Reactive power
Normally, the power supply provides only a part of Q, and the remaining amount needed by the capacitor is produced to raise the cosφ to help P increase.
Classification of compensating capacitors
Power compensating capacitors are classified in several ways, the most common of which are by construction and by voltage.
Classification of compensating capacitors by structure
Dry compensating capacitors are long, compact cylindrical compensating capacitors that are popular in industrial electrical cabinets. Dry compensators are used for power systems with a voltage harmonic level of < 3%, and the power quality is quite good. The power range of dry compensating capacitors ranges from 1kVAr up to 50kVAr.

Oil compensating capacitors are rectangular box-shaped compensating capacitors, with high strength and diverse capacities. Oil compensating capacitors are used for all power compensation systems, especially in circuits with high power, poor power quality and large harmonics due to good harmonic coordination. The common power range of oil compensating capacitors is 10kVAr to 50kVAr.
Classification of compensating capacitors by voltage
When classifying compensating capacitors by voltage, there are 3 types: low voltage, medium voltage, and high voltage used for 3 types of power grids.
Low-voltage compensating capacitors
Low-voltage power compensation capacitors are used for low-voltage power grids with low cosφ capacity, which is used to compensate for the reactive power, improve the operation efficiency of the equipment and reduce the cost of electricity bills. There are 2 most common types of low-voltage compensating capacitors: 1-phase low-voltage compensating capacitors and 3-phase low-voltage compensating capacitors.
1-phase capacitors have 230V and 250V voltage types. 3-phase compensating capacitors have a voltage type of 250V for 220V circuits, the 415V type is used for standard voltage systems of 380V and the 440V type is used for higher voltage systems. There are also 480V or 525V types,...

In terms of structure, the 3-phase compensator has 3 poles against the source instead of 2 poles as on the 1-phase compensator. In addition, the 3-phase capacitor is equipped with an explosion-proof capacitor – a mechanism that automatically shuts off the capacitor power to compensate when overloaded to avoid capacitor explosion.
Medium Voltage Capacitors
Medium-voltage compensating capacitors used in medium-voltage power grids are capable of charging and discharging to stabilize the source voltage and compensate for the reactive power of the equipment. Medium voltage compensators have voltage levels from 3kV to 35kV and are divided into two types: 1-phase 2-ceramic type and 3-phase 3-ceramic type.
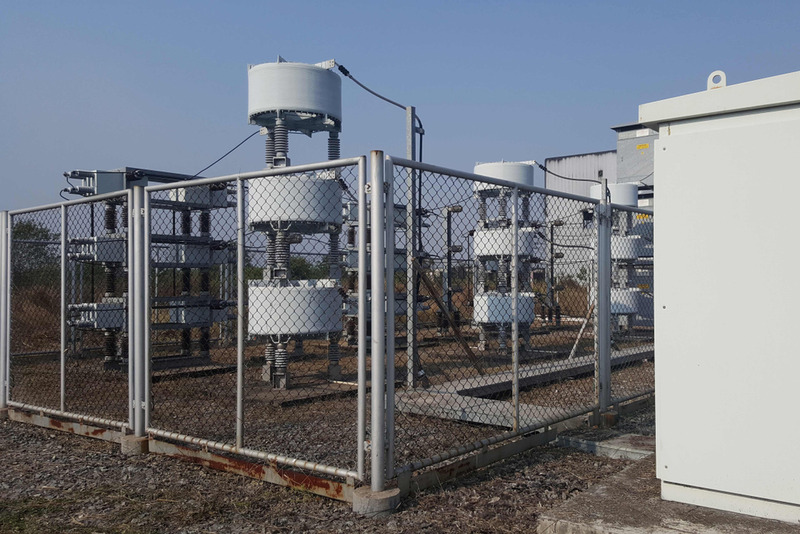

High voltage compensating capacitors
A high-voltage compensating capacitor is an electrical device used to compensate for the reactive power generated by inductive devices such as electric motors and transformers in a high-voltage power system. A high-voltage power system usually has a voltage from 110kV to 500kV.
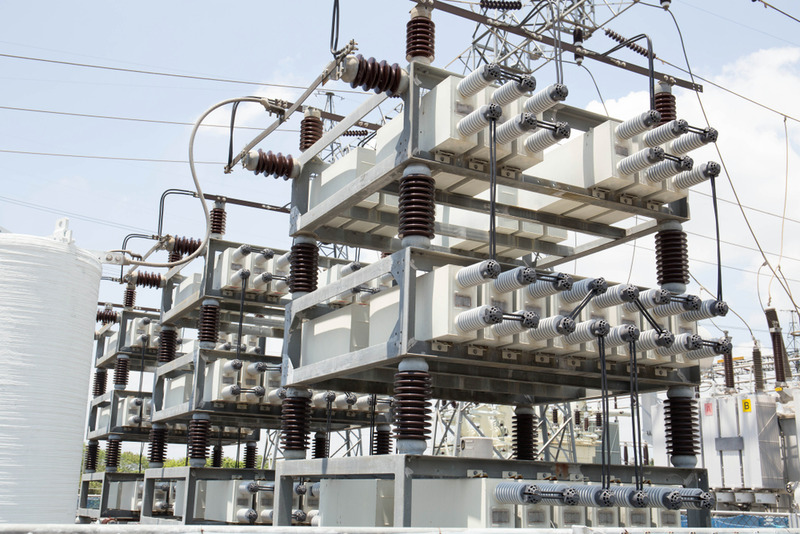

Application of compensating capacitors in practice
A simple way to install a compensating capacitor is to connect it directly to the electrical system in parallel with the load line to compensate for the reactive power. This is a static compensation or background compensation. But now this compensation method is no longer popular and is only used to compensate for small systems with a capacity of a few tens of kW.
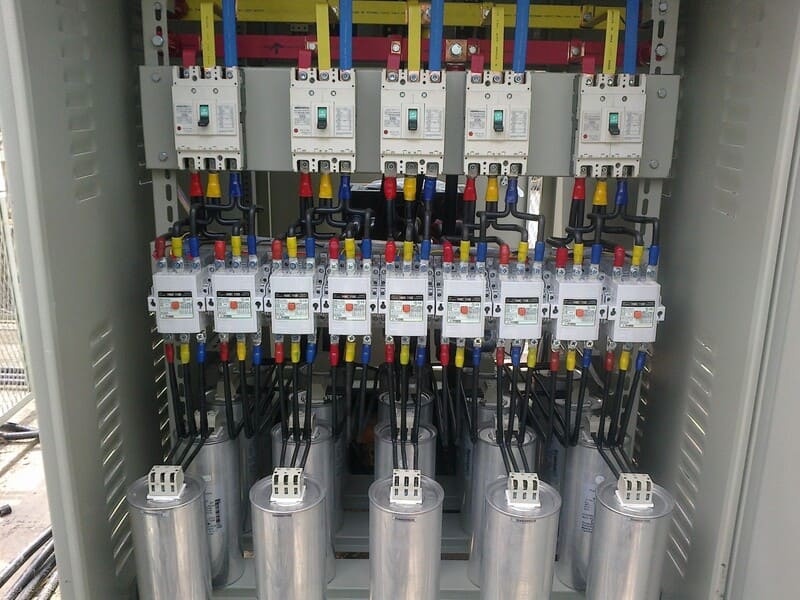

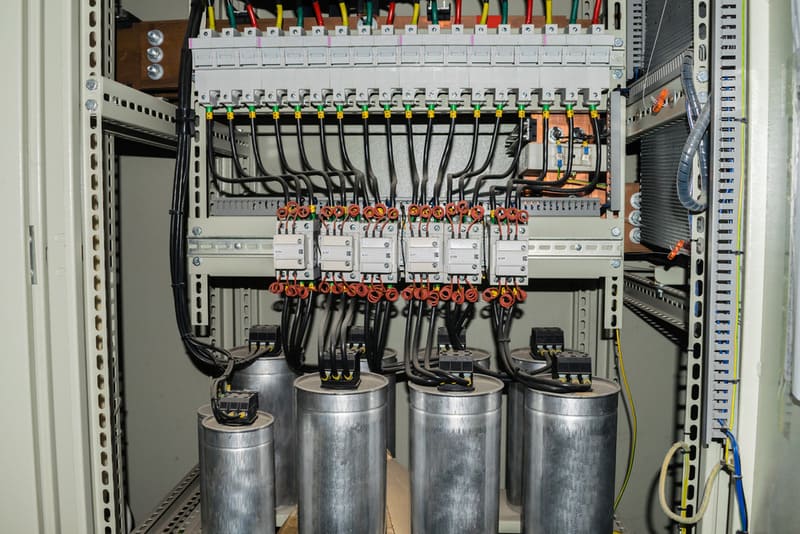
The most common application of electrical compensating capacitors is to install in a reactive power compensating capacitor cabinet with multiple capacitor levels. This cabinet is controlled through contactors and compensating capacitor controllers to automatically shut off and off the electrical compensating capacitors. The inside of the cabinet usually includes: Compensating capacitor controllers, breaker levels, contactors for capacitor levels, compensating capacitors, often with additional resistance coils but need to be selected to avoid the case of installing the wrong resistance coil that will cause counter-effects, power meters, capacitor housings, wires and other materials.
Formula for calculating capacitor capacity
In order to choose the right power compensation capacitor for the load, it is necessary to calculate the P power of the load and the cosφ coefficient:
- Power factor of load: Cosφ1 -> φ1 -> tgφ1 (before compensation, cosφ1 is small and tgφ1 is large).
- Power factor after compensation: Cosφ2 -> φ2 -> tgφ2 (after compensation, cosφ2 is large and tgφ2 is small).
- Reactive power to be compensated: Qb = P*(tgφ1 – tgφ2)
Example with load with power P = 150kW
- The power factor before compensation is cosφ1 = 0.75 → tgφ1 = 0.9.
- The power factor after compensation is Cosφ2 = 0.95 → tgφ2 = 0.35.
- The reactive power to be compensated is Qb = 150*(0.9 – 0.35) = 82.5 kVAr
If we do not know the nature of the load and capacity, we will choose the compensated capacity according to experience, which will usually compensate 50% to 60% of the transformer capacity.
How to choose the right power compensator for your system
How to choose a capacitor to apply in different power systems greatly affects the performance of the capacitor as well as that power system in the future.
Installing compensating capacitors for small systems
The characteristics in small production systems are that the power is not high, the system is not too complex and there are almost no harmonics, and the reactive power is low. Whether or not to install capacitors depends on the area where the power system is located and the financial balance.
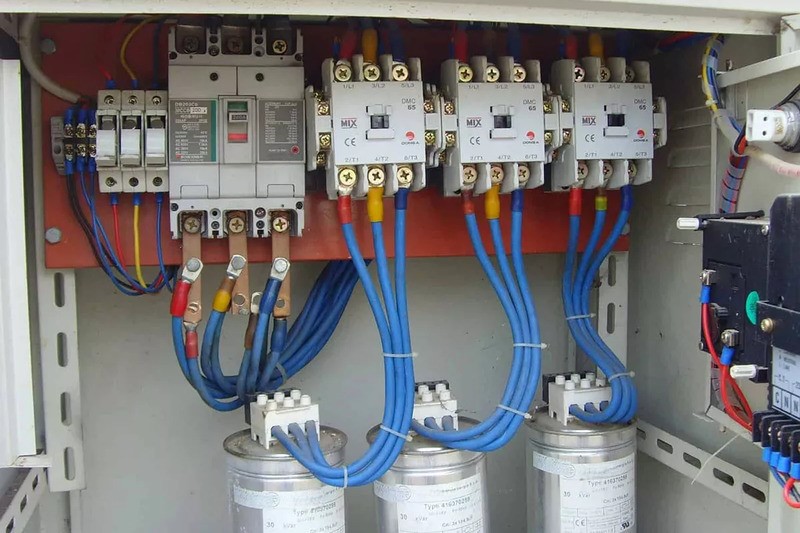

For small electrical systems, installing a compensating capacitor with the static compensation method is suitable. The compensating capacitor cabinet in this case has a fairly simple structure consisting of a cabinet shell, 1 breaker and 1 low-power compensating capacitor not greater than 10kVAr.
Fitting compensating capacitors for medium systems
The characteristics in the power system for production are medium power, medium reactive power, harmonics but small. This system definitely needs compensating capacitors to save electricity and if you don't want to be fined, you need to install compensatory capacitor electrical cabinets with many levels.
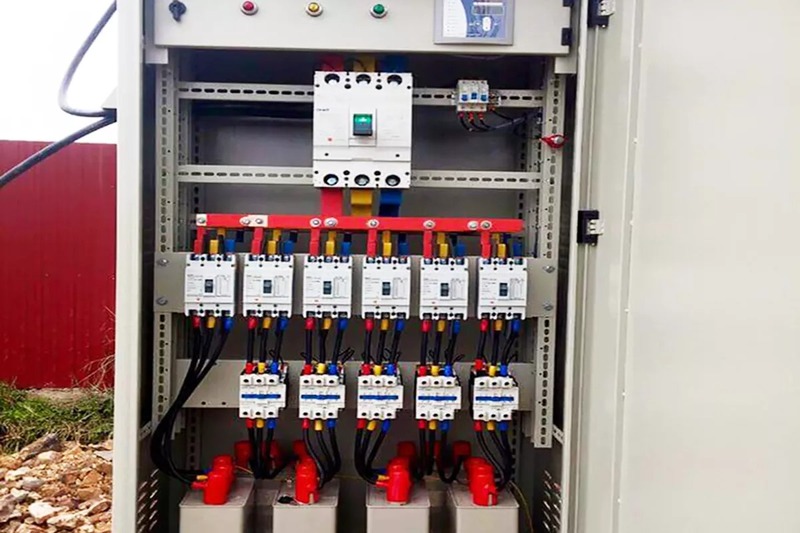

Most units choose automatic compensating capacitors to optimize operation and increase accuracy when switching capacitors, increasing the durability of the equipment. The automatic capacitor cabinet includes: Cabinet housing, automatic controller, breaker for each capacitor level, contactor, compensator capacitor and supporting devices.
Mounting Capacitors for Large Systems
In high-capacity power systems, high power consumption and reactive power, there is often the installation of a separate substation. Installing a compensating capacitor cabinet for this system, in addition to the requirements such as for medium system cabinets, the classification of compensating capacitors is more complicated, the capacitor capacity is higher, and most of the time, it is necessary to install more resistance coils to minimize harmonics falling on the capacitor, limit the explosion of the compensating capacitor, help increase the life of the capacitor and help the capacitor operate normally stably and for a long time.
Instructions for Matchmaking
There are 2 popular methods of installing power compensation capacitors in industrial electrical cabinets today: static capacitor installation and condensation installation.
How to fight electrostatic capacitors
The static offset capacitor method uses one or more parallel offset capacitors. The static compensation mechanism produces a constant amount of compensation power under all conditions. The user can control the capacitor manually or semi-automatically. The advantage of this method is that it is easy to install, the cost is cheap, but the efficiency is not high, and it is easy to lose energy.
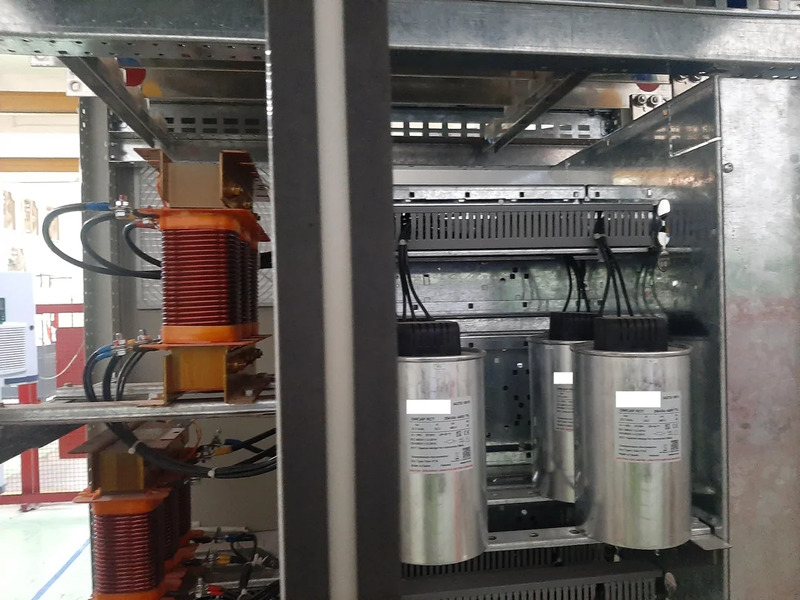

Electrostatic Capacitor Installation Steps:
- Step 1 – Install the breaker: Install the breaker in the correct position in the compensating capacitor cabinet and correctly connect the phase and neutral wire circuits to the power and load terminals.
- Step 2 – Connect the compensating capacitor to the breaker: Match the correct cathode – positive terminal of the capacitor to the phase – neutral wire, then connect the capacitor to the breaker.
- Step 3 – Attach the neutral wire (if applicable): Connect the neutral wire from the compensator to the neutral wire of the source.
- Step 4 – Fix the compensating capacitor: Attach the compensating capacitor to the bracket or rail on the electrical cabinet.
- Step 5 – Test and operate the cabinet: Check the voltage at the connection points, observe the operation of the capacitor after powering it up, and monitor the power and voltage indicators,... of the system.
How to fight electrodynamically compensated capacitors
The dynamic compensating capacitor method is to use a compensating capacitor with an automatic controller, which increases the accuracy of operation, automatically monitors the indicators, and changes the capacitor capacity as needed. This method helps the power system achieve high capacity stability, limiting excess compensation but high cost.
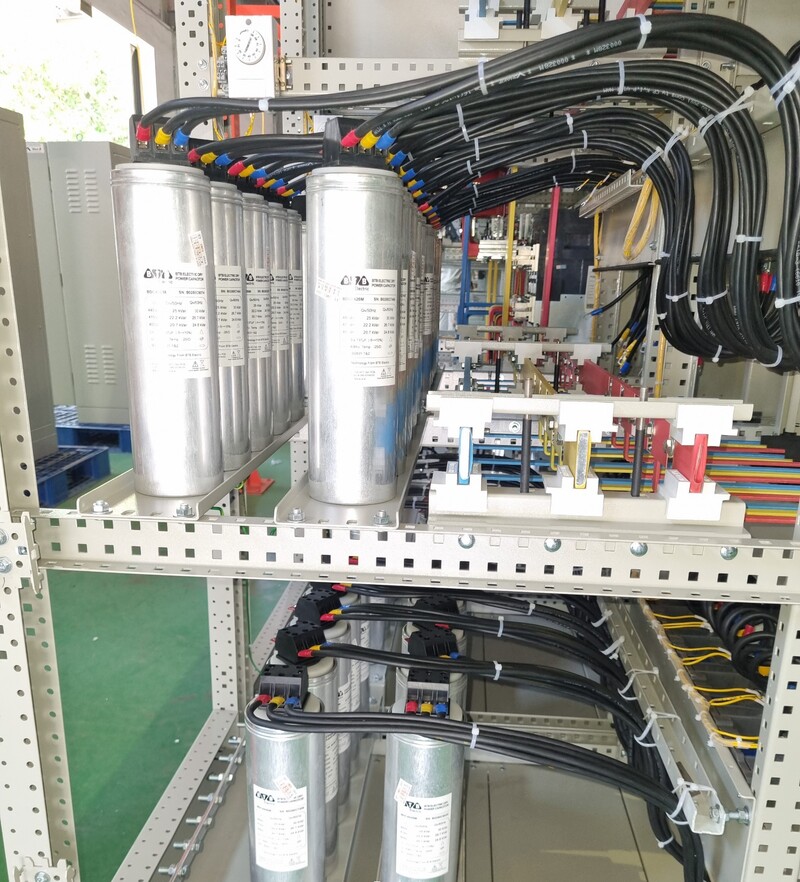

The steps to install the electrostatic capacitor are similar to those of the electrostatic system, besides the additional step of connecting the capacitor to the control system and aligning the capacitor capacity. After the installation is completed, it is necessary to check the power system, the operation of the compensator capacitor and the equipment, and test the automatic control.
Some errors when installing compensating capacitors
- Capacitor failure to automatically compensate for power: The error is caused by some types of relays that reset themselves to their default values and need to be reset accordingly.
- Capacitor failure to calculate cosφ value: Error caused by improper connection of current signal or voltage signal to the relay. It is necessary to rematch the diagram of the relay and try to load it again.
- Default auto-reset relay error: It is necessary to reduce the MBA voltage differential or replace the relay with a new one.
- Capacitor Fault Exploded: Incorrect setting of voltage, current, or contact connection errors.
- Relay error cannot control the compensator capacitor when the current is too small: Errors caused by large current variables or large current variable angle errors. It is necessary to change the current variable with a variable ratio suitable to the load and error that meets the general standards of measurement techniques.
How to discharge the power to the compensator capacitor
Before repairing, transporting or maintaining or replacing the capacitor, it is necessary to discharge the capacitor to ensure safety and avoid fire and explosion. The only way to discharge power to the compensating capacitor is to insert the resistor into the terminals and discharge the power.
Absolutely do not use spontaneous condensation discharge measures such as using screwdrivers or crocodile clamps. These methods are all manual, without controlling the amount of discharge, it is easy to cause short circuits, dangerous for enforcers.
After discharging the capacitors, it is necessary to check the voltage between the capacitor terminals with a multimeter, ensuring that the voltage reaches 0. When discharging, it is necessary to equip protective clothing, the discharge location is cool, away from water sources and flammable materials.
Select BTB Electric Capacitors
BTB Electric dry compensating capacitors are 3-phase dry compensating capacitors, with a power range from 5 kVAr to 30 kVAr, suitable for a variety of compensating capacitor electrical cabinet systems. The product only loses less than 0.2W/kVAr, and the durability reaches 130,000 operating hours. The maximum allowable current through the capacitor is 1.5 In, the maximum starting current is 200 In, and the capacitor is equipped with an overvoltage circuit breaker.
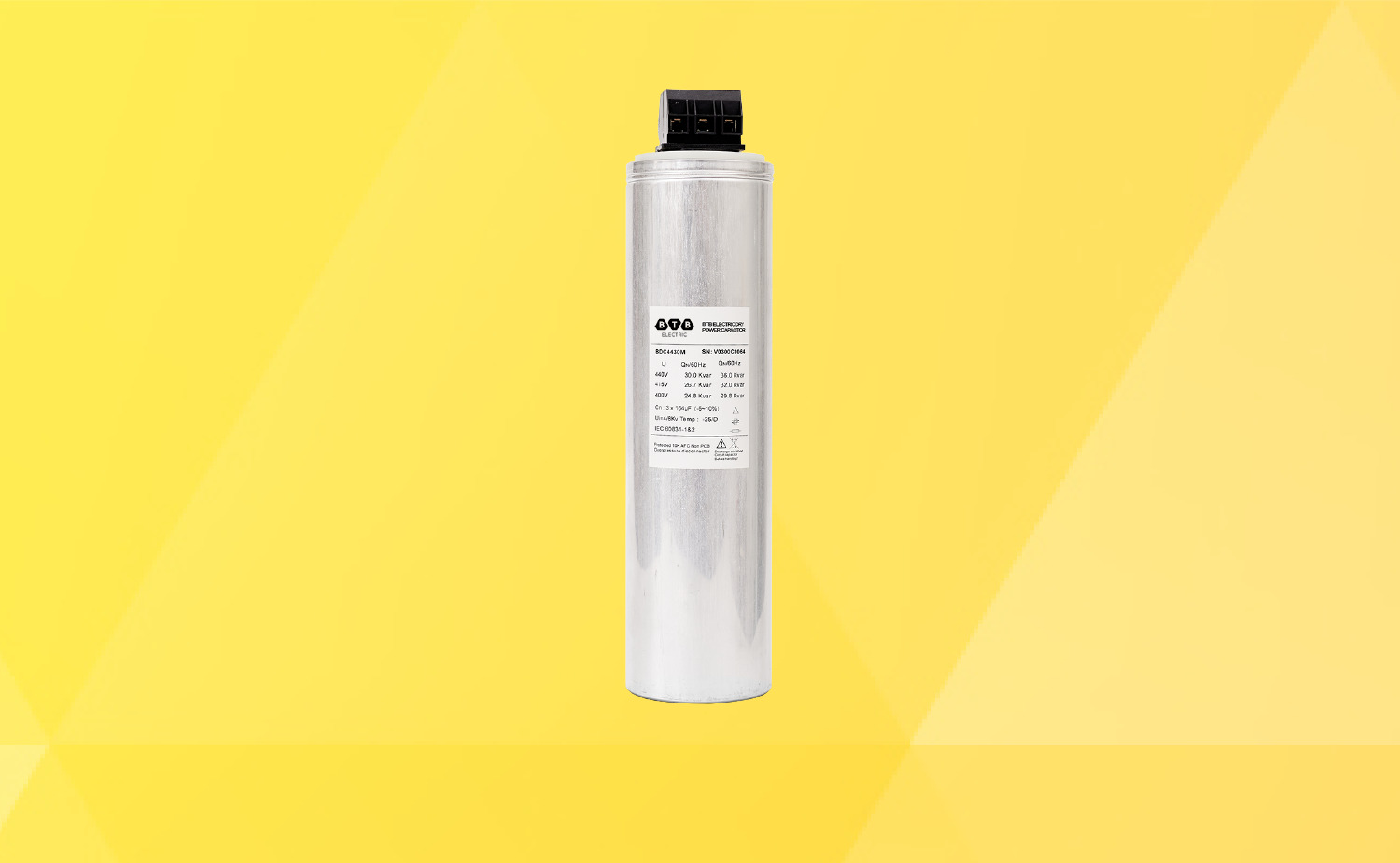

BTB Electric's reactive power compensators have been present in many capacitor compensating cabinet systems at medium and large factories across the country, which are highly appreciated by customers for product quality and good warranty policies. Refer to product information at: https://btb-electric.com/vi/tu-bu/
Some questions about capacitors
Question 1: Do compensating capacitors save electricity?
Answer: A compensating capacitor is a device that consumes electricity, which is not capable of saving electricity. However, the compensating capacitor helps to improve the cosφ power factor, helping to reduce the system's monthly penalty electricity bill.
Question 2: Does household electricity need to use a compensating capacitor?
Answer: A small-scale, purely domestic household electrical system will not need to use a compensating capacitor. This device is suitable for 3-phase current used for production and commercial use.
Question 3: Should I choose dry or oil compensating capacitors?
Answer: Small power systems should use dry compensators to save cost and installation area while still ensuring power quality. With a large-scale power system, priority is given to using oil compensation capacitors with the advantages of durability, operation with large capacity, and poor power quality.