24-12-2025
What is MCCB? Structure, classification and application
MCCB is a block circuit breaker used to protect electricity from the risk of overload and short circuit of the line. MCCB is applied in many areas of life, mainly in production and business. Specifically, what is MCCB, how is its structure and what is its use will be answered by BTB Electric in the following summary article.
Function of MCCB
MCCB (short for Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) or block-type circuit breaker is an automatic circuit breaker widely used in industrial electrical systems. MCCB is quite large in size with 2-3 or more pairs of poles and only 1 single lever, compared to the MCB structure with 1 or more interconnected levers. Some MCCB lines have the ability to adjust the cutting current or have an electronic screen for remote control.
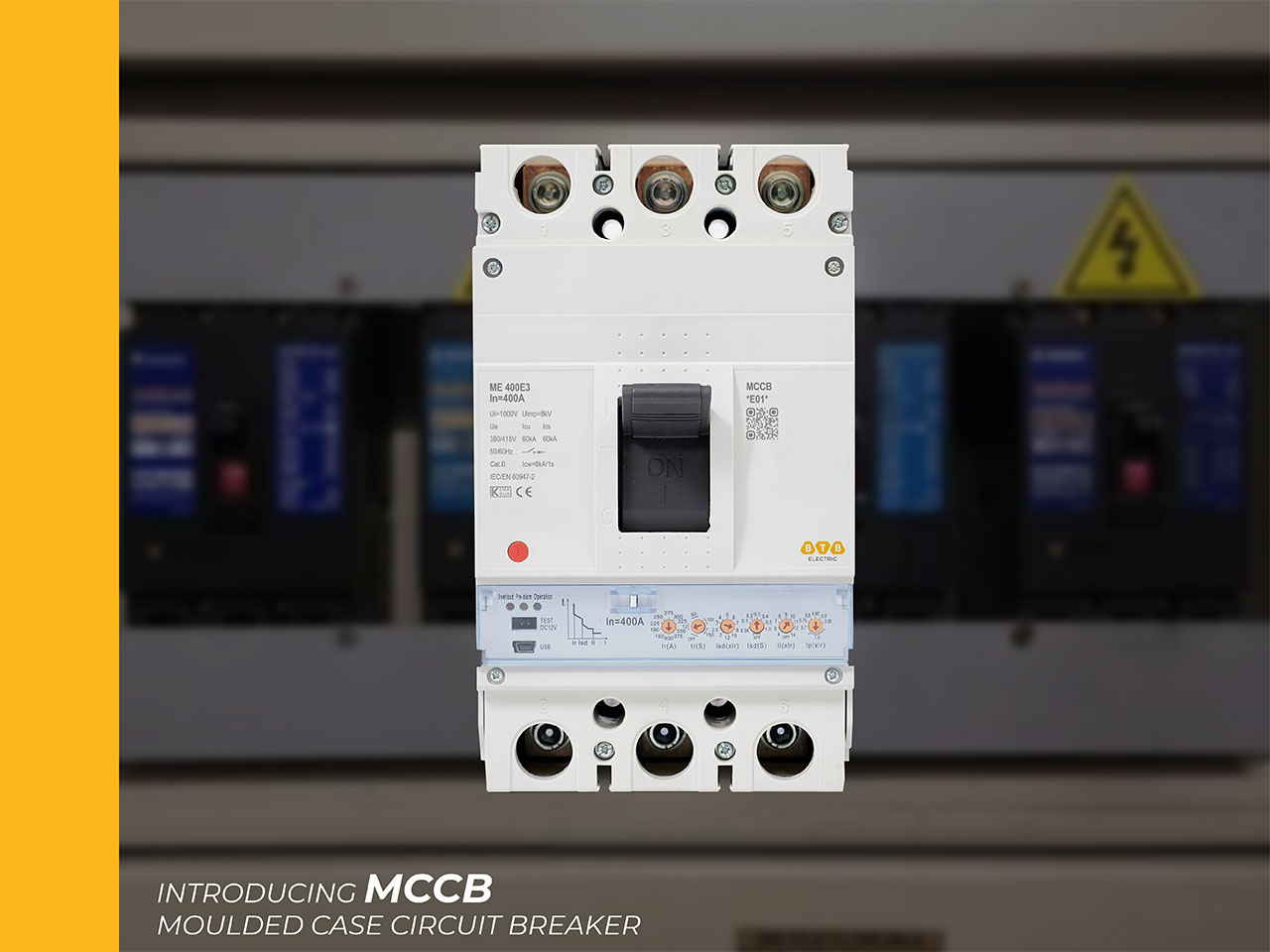

MCCB has three main functions:
- Protects circuits against overload – when the rated current is abnormally high, preventing the line from heating up. MCCB uses a bimetallic strip or heating element in the breaker to heat up when an overload current flows through it, bending and causing the circuit to trip.
- Protects the circuit when there is a short circuit, helping to avoid damage to the electrical system. MCCB uses a magnetic circuit breaker, interacting with the magnetic field generated by the short circuit current to cut off the power.
- Controlling the electrical circuit with the on-off mechanism is very important when the electrical system needs to be checked, maintained, repaired or upgraded.
Structure of MCCB
MCCB has a traditional circuit breaker structure, mainly consisting of the following parts:
- Frame: The outer shell of the MCCB, made of high-quality plastic, sturdy, durable, with good insulation and heat insulation.
- Trip Actuator: Used to turn the device on or off, holding the handle in the correct position when switched on. If there is a fault, this mechanism will automatically turn off and the MCCB will have to be switched on or off manually.
- Trip unit: MCCB trips when overload or short circuit is detected.
- Lever: Used for MCCB maintenance, the technician will use the lever to manually turn the device on and off.
- Tripping mechanism: Contact point for wires, ensuring tight connection.
- Arc arrester: Used to separate the arc into small pieces when the MCCB breaks the normally closed contact and creates an arc.
- Push button switch: Added to MCCB to perform tripping when required.
- Contacts: MCCB has 2 contact levels: static contacts and moving contacts.
Technical parameters on MCCB
Some important parameters on MCCB you need to know are Ui, Ue, Uimp, In, Icu and Ics. Specifically, the roles of these parameters are as follows:
- Ui – Rated insulation voltage (V): The maximum current value that the MCCB can withstand under laboratory conditions. In practice, the current withstand value of the MCCB can be lower than Ui to increase safety.
- Ue – Rated working voltage (V): Continuous operating voltage value of MCCB, usually coincides with system voltage.
- Uimp – Rated impulse voltage (V): The highest impulse current value that the MCCB can withstand when there is a current fault such as overload, short circuit or lightning strike.
- In – Rated current (A): The highest current value that the MCCB can withstand in the event of an electrical fault or the cut-off current level, the allowable limit for current to pass through.
- Icu – Maximum circuit breaking capacity (kA): When the current exceeds this value, the MCCB cannot automatically break the circuit but will activate the protection mechanism.
- Ics – Actual short circuit current (kA/%Icu): MCCB will operate when fault current occurs within this threshold and will have other protection mechanisms if current exceeds this value. The higher Ics, the better MCCB.
Operating principle of MCCB
Most MCCBs operate on a thermal mechanism to detect overloads, trip the circuit, and disconnect the power. MCCBs have thermal overload protection, which means that when the current exceeds the rated limit and the contacts begin to heat up, the circuit will automatically disconnect. The thermal disconnection feature of MCCBs has a time delay, allowing for short-term and controlled overloads.

Along with that, the operating principle of MCCB can be based on electromagnetic induction and instant response time. With this mechanism, MCCB detects very quickly the faults on the current and immediately disconnects the circuit. At the same time, these MCCB lines are equipped with the feature of dispersing the electric arc inside in case of too fast reaction.

Many types of MCCB can be controlled remotely via a controller, replacing manual operation by hand. This feature is useful when maintaining and repairing electrical systems, controlling the current status well and protecting the safety of electrical technicians during repairs.
MCCB’s classification
MCCB product line from BTB Electric is of high quality, meeting IEC 60947-2 standards with 4 codes:
- MF: Fixed circuit breaker – protection relay T01; rated current range (In) from 20A to 800A; short circuit breaking current at (Ue) = 690V is 25kA, 36kA, 50kA and 85kA.
- MT: Thermal control mechanism circuit breaker – protection relay T02; rated current range (In) from 20A to 800A; short circuit breaking current at (Ue) = 690V is 18kA, 25kA, 36kA, 50kA and 60kA.
- ME: Electronic mechanism circuit breaker – protection relay E01; rated current range (In) from 320A to 1600A; short circuit breaking current at (Ue) = 690V is 60kA and 65kA.
- iME: Electronic mechanism circuit breaker – protection relay E01 – remote control; rated current range (In) from 320A to 800A; short circuit breaking current at (Ue) = 690V is 60kA and 75kA.
 |
 |
Outstanding features of MCCB products from BTB Electric:
- High efficiency and class A selectivity
- Made from environmentally friendly ingredients, all recyclable.
- Designed for safety in all situations
- Current frame from 125A to 1000A
- Applicable standards: IEC/EN 60947-2
- Quality certificate: DEKRA
For details on specifications, product catalogues, drawings and certificates, please refer to the MCCB BTB Electric product page.
In addition, MCCBs can be classified according to their operating range, denoted as B, C, D, K, Z respectively. Specifically, the differences between these types are as follows:
| MCCB Type | Impact line | Time of impact | Function | Application | Mutation |
| B | 3 – 5 times rated current | Maximum 13 seconds | Resistive load | Lighting, resistance | Short |
| C | 5 – 10 times the rated current | Maximum 5 seconds | Inductive load | Used for industrial and commercial electricity | Fit |
| D | 10 – 20 times the rated current | Maximum 3 seconds | Inductive – capacitive loads | Used for industrial and commercial electricity | High |
| K | 8 – 12 times rated current | Maximum 5 seconds | Inductive loads and high starting current motors | Used for industrial electricity | High |
| Z | 2 – 3 times the rated current | Maximum 5 seconds | Suitable for medical devices | Protects highly sensitive equipment such as semiconductor devices | Very low |
MCCB equipment is a mandatory element for industrial and commercial electrical systems to operate smoothly and ensure system safety.
Applications of MCCB
MCCB is mainly used in industrial electrical systems. Thanks to its design and many superior features compared to conventional circuit breakers, this line of circuit breakers is very suitable for specific applications in industrial electricity with high safety and precise operation.

Specifically some applications of MCCB:
- Welding applications: Some industrial welding machines require very high currents, requiring the use of a separate MCCB.
- Capacitor bank protection application: Capacitor bank is an important part of the power system, determining the ability to correct the power factor. MCCB helps reduce the input current to the capacitor, thereby reducing electricity costs.
- Main power supply protection application: The power circuits supplying large distribution boards have very high rated currents, requiring the use of MCCB for protection.
- Protection application for generators: Generators provide hundreds of A of current, have the risk of conflict with the grid, so need to be protected by MCCB against incidents.
Distinguishes between MCCB and MCB
Looking from the external design, it can be seen that MCCB is “more massive” than MCB. Correspondingly, the parameters on the block circuit breaker line are superior to those of the small circuit breaker.
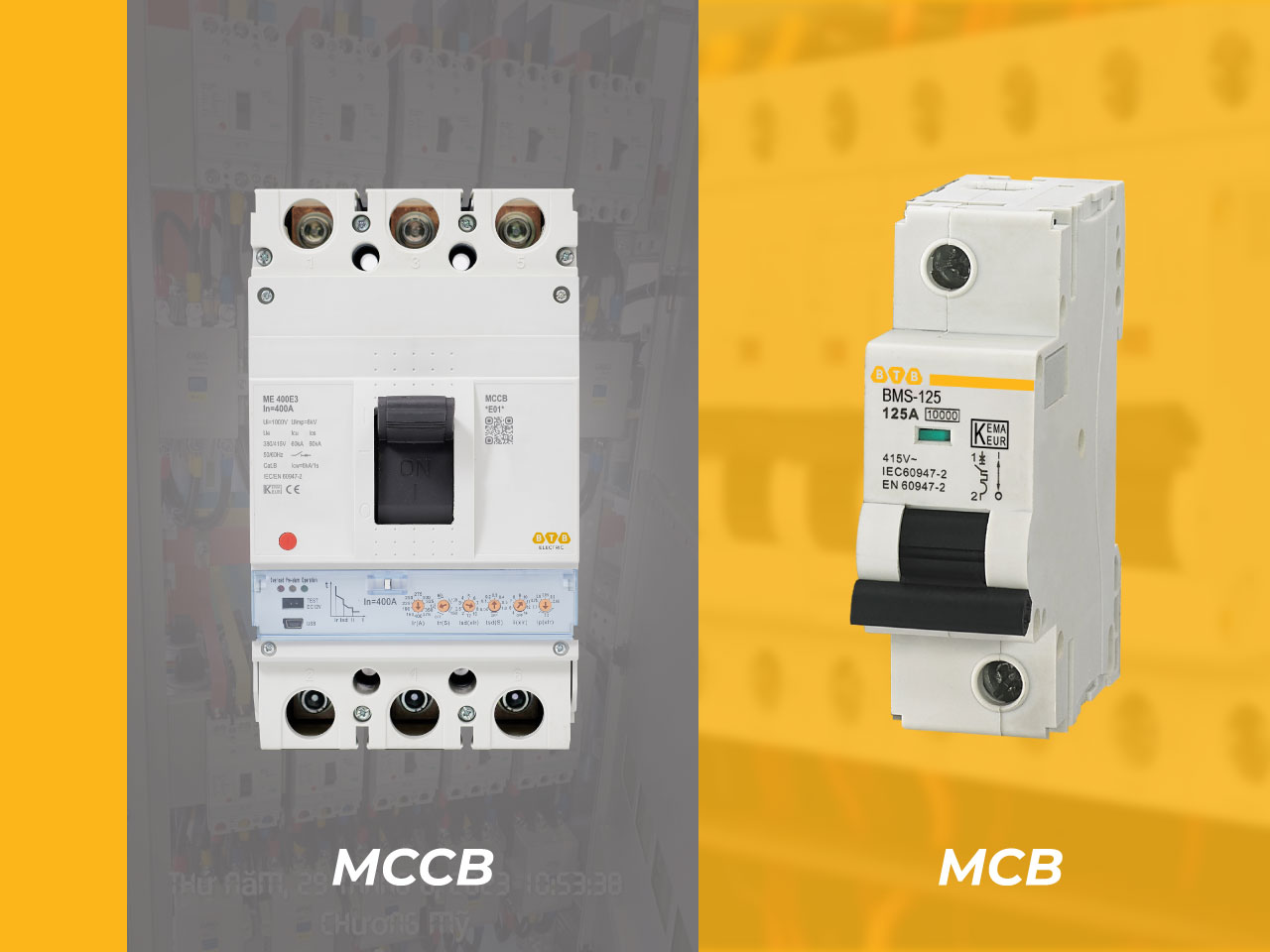

MCCB is mainly used for industrial electrical systems (3-phase electricity), for devices with high power current, current reaching 2500A or some special cases. MCB is widely used in household electrical networks and low-power electrical devices, maximum current about 125A.
MCBs come in many types, from 1-phase 1-pole to 3-phase 4-pole. While MCCBs come in only 2 types: 3-phase 3-pole and 3-phase 4-pole.
Notes when choosing to install MCCB
The basic principle when selecting MCCB is the formula IB < In < IZ, in which:
- IB: maximum load current
- In: rated current of MCCB
- IZ: maximum allowable current through the conductor
Note that in practice, In is usually 25 – 30% higher than IB to prevent the risk of sudden voltage increase in case of a problem.
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the formula ISCB > ISC, ISCB is the maximum current that MCCB can cut and ISC is the short-circuit current.

In addition, when choosing a block circuit breaker, you need to pay attention to the compatibility of the device with the electrical system with the option of having or not having a neutral wire. If there is a need to periodically maintain and upgrade the electrical system, the remote control feature of the MCCB is very important and should be equipped.
Some questions
Question 1: Can MCCB be used for household electricity?
Answer: MCCB is mostly used for 3-phase 380V electricity. Some 1-phase 2-pole MCCB models can be used for household electricity, but the cost will be higher if using MCB with equivalent technical specifications.
Question 2: Does MCCB have leakage protection?
Answer: MCCB does not have the function of preventing leakage current or electric shock. MCCB only has the function of preventing overload and short circuit.
Question 3: What are the 4 types of MCCBs of BTB Electric?
Answer: BTB Electric's MCCBs include 4 types: fixed protection type (symbol MF), thermal protection type (symbol MT), electronic protection type (symbol ME) and electronic protection type with LCD display (symbol iME). MF and MT types are quite popular, low investment cost but do not have remote control function. ME and iME types have remote control function, technical parameter customization and higher investment cost.
Question 4: Can MCCB be used to replace ACB?
Answer: ACB or air circuit breaker, specially installed at the low voltage source, right after the transformer station. The normal switching mechanism of MCCB cannot meet the requirements when placed here. Therefore, MCCB should not be used to replace ACB.