24-12-2025
What is Resistance Coil? Construction, Function and Application
In areas with poor power quality, high-order harmonics appear that adversely affect the operation of electrical equipment, causing these devices to break down quickly and consume more energy. In particular, power compensation capacitors are devices that are sensitive to harmonics, damaged very quickly when harmonics are affected.
Resistance coils with harmonic filtering ability for compensating capacitors are preferred for most electrical systems, the purpose of which is to reduce harmonics thereby increasing the efficiency of using electrical equipment. In the article below, let's learn about the structure, function, operating principle and application of electrical resistance coils with BTB Electric.
What is Resistance Roll?
A resistance coil is one or more coils with constant inductance (without L>>R steel core), large capacity, wound around an iron core. This type of device is capable of limiting short-circuit current, limiting harmonics, and maintaining a certain voltage value for the circuit if there is a change in current.
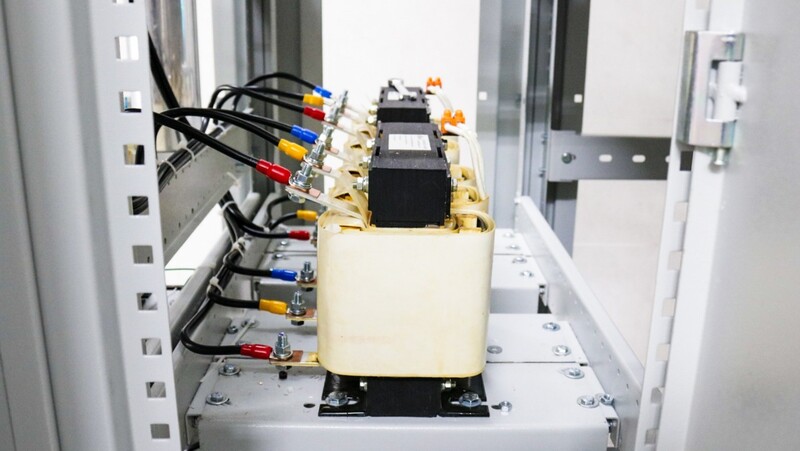

Particularly in the current low-voltage power network (electricity used), there are a lot of loads when operating that emit a voltage much higher than the frequency of 50Hz, which is harmonics. These harmonic components change the voltage and frequency parameters, making the current no longer have the same properties as it was originally. Especially if there is harmonic resonance of the 5th - 250Hz and 7th - 350Hz harmonic resonances, they are very harmful to the electrical element. Therefore, in order for electrical equipment to operate at a standard level (with 3-phase electricity of 380V - 50Hz), the electrical resistance coil is the solution to eliminate the above situation.
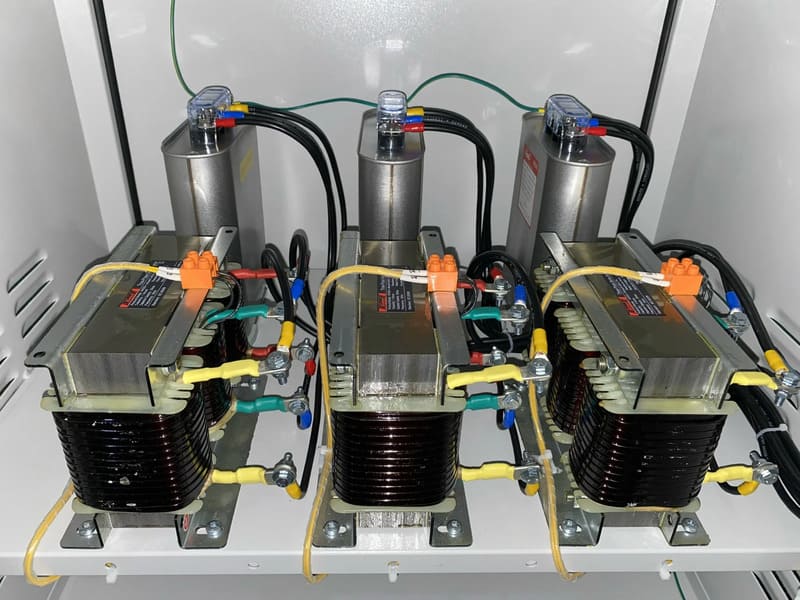

Resistance coils are familiar equipment in industrial electrical cabinets, ensuring that the electrical system is operated more efficiently. Especially in cases where the current is distorted a lot, the voltage stability of the resistance coil is very important.
Electrical resistance coil construction
The resistance coil is composed of 1 copper coil wrapped around the ferromagnetic core. The conductor cross-section, the number of wire turns, and the size of the iron core are proportional to the inductance in the resistance coil. The inner iron core is a solid core or foil core, which has the function of enhancing the magnetic field of the coil current. The magnetic field generates induction to inhibit current variation through the resistance coil and limit harmonics.
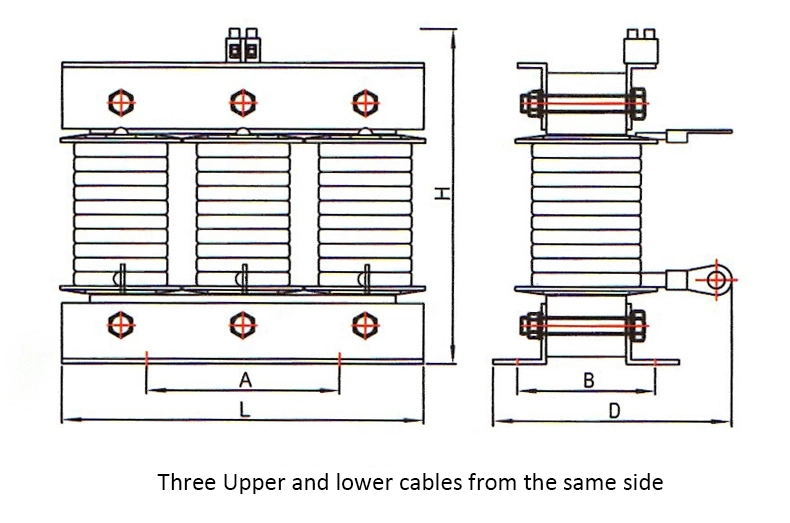
In addition, the resistance coil has an additional heat dissipation system, fuse and outer enclosure. Between the shell and the coil can be a layer of immersion oil or insulating paint to protect the coil resistantly.
The working principle of the resistance coil
In an AC circuit, the inductance is directly proportional to the frequency of the current. The greater the frequency, the greater the resistance, so the smaller the current flowing through the resistance coil. Therefore, this property is applied to electrical resistance coils in the suppression of high-order harmonics.
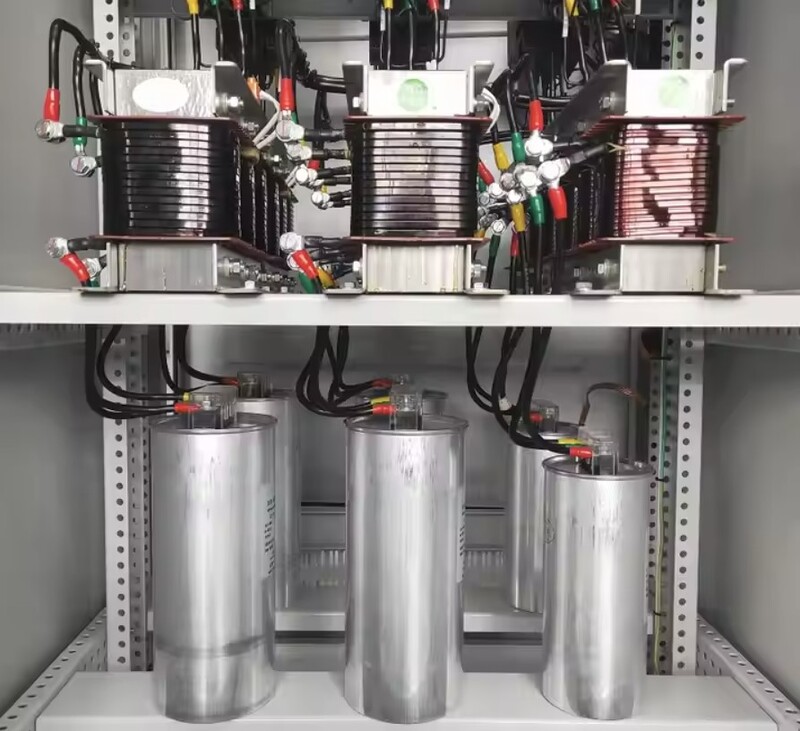

Electrical resistance coils are used in combination with reactive power compensation capacitors for high-order harmonic filtering. The higher the harmonic frequency, the greater the resistance of the resistance coil, so the smaller the harmonic current through the resistance coil, which minimizes the impact of harmonics on the power system.
The working principle of the resistance coil is based on the principle that the resistance is inversely proportional to the current frequency and the inductance is directly proportional to the current frequency. The resistance coil is connected in series with an electric compensating capacitor to filter harmonics of order 5 and order 7. When the power contains 5th and 7th order harmonic components, the current through the compensating capacitor will be greater than the alternating current without harmonics. So this device will generate an inductive voltage that is out of phase with the current, reducing the current through the compensating capacitor, thereby minimizing the impact of harmonics on the power system.
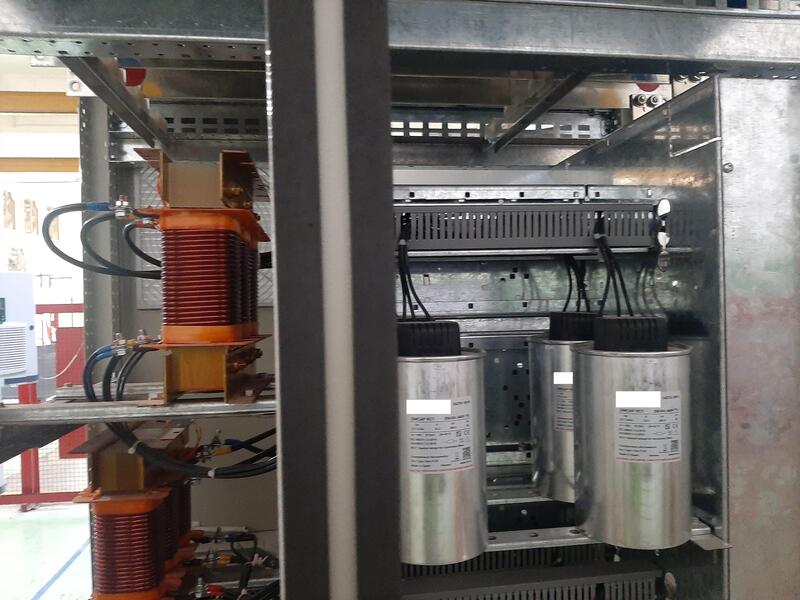

In order to stabilize the output current of the inverter, the resistance coil will be installed in the industrial inverter. This helps the electric motor work more smoothly, increasing durability when changing speed and reversing.
Function and application of resistance coil
The resistance coil has 2 main functions: inverter protection and industrial electrical equipment protection.
Inverter Protection
An important function of the resistance coil is to protect the inverter of the circuit segment. Inverter output (DC) resistance coils and inverter input (AC) resistance coils are 2 types of resistance windings used for inverters. Due to the constant characteristics of resistance windings, the device helps reduce the current passing through the inverter, thereby helping the inverter and motor to operate smoothly even if there is a change in speed or frequency.
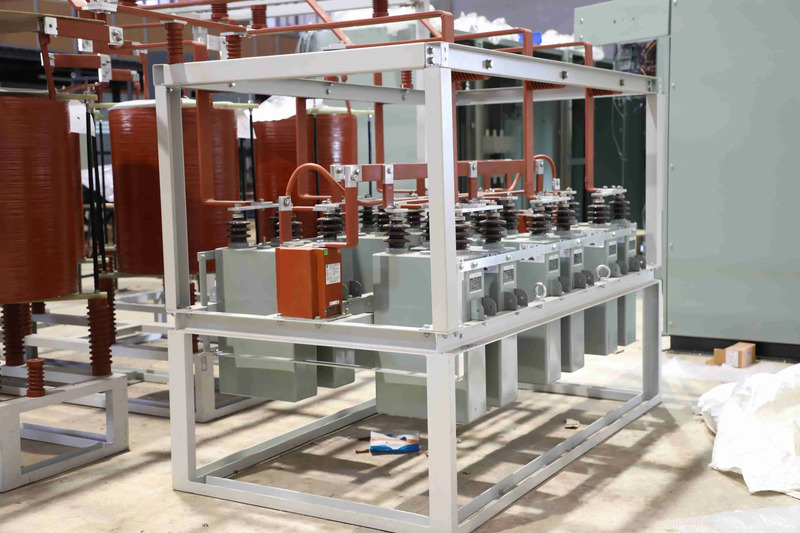

Industrial Electrical Equipment Protection
With the characteristic of being a passive electrical device, capable of obstructing alternating current, the resistance coil has the function of protecting electrical equipment in general. Electrical resistance coils are used in combination with compensating capacitors to filter high-order harmonics, protect compensating capacitors and circuit switchgear.
Electrical Resistance Coil Classification
There are 3 ways to classify resistance coils which are by voltage, by construction and by application.
Classification of resistance coils by voltage:
- Low Voltage Resistance Coil: Used for 440V - 1000V power system, application for power of factories, factories, enterprises,...
- Medium Voltage Resistance Coil: Use for 1000V magnetic power system, application in power stations.
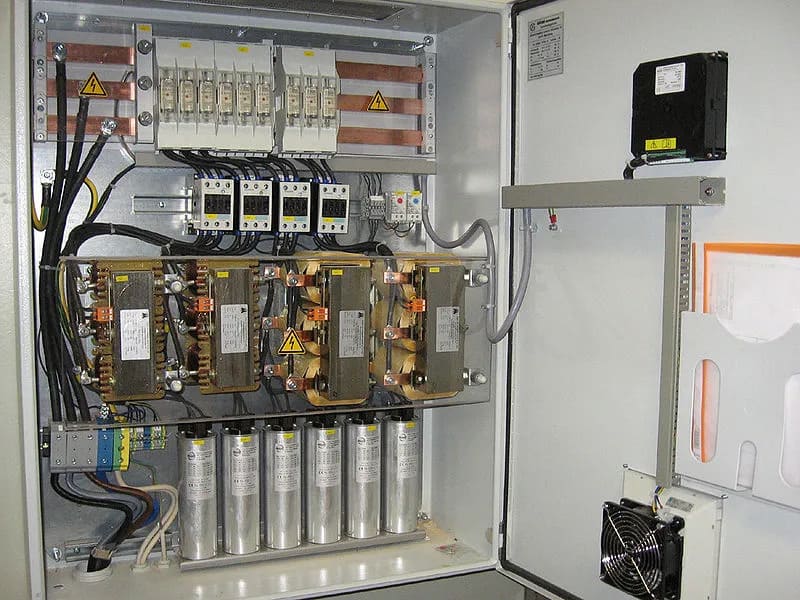

Classification of resistance coils by structure:
- Oil-free resistance coil: The coil in the resistance coil is wrapped around the iron core and coated with insulating paint.
- Oil Immersion Resistance Coil: The coil in the resistance coil is wrapped around the iron core and is impregnated with insulating oil.
Classification of resistance coils by application:
- Conventional resistance coil: Used to protect compensating capacitors, relays, contactors and some other equipment to eliminate harmonics, increase the quality of the power grid.
- Inverter Protection Resistance Coil: Specialized for inverter protection, including input resistance (AC) and output resistance (DC) coil.
How to choose an electrical resistance coil
Before choosing a resistance coil, you need to measure the existing harmonics in the area, thereby determining the harmonic level of the resistance coil to be installed is 6%, 7%, 13%, 14% or higher. Choosing a resistance coil with inappropriate parameters is the cause of overvoltage, explosion of compensating capacitors and failure of electrical equipment in the system. In addition, it is necessary to clearly know whether the system voltage is low or medium voltage to choose a compatible resistance coil. Most resistance coils are installed with electric compensating capacitors, so the resistance of the capacitor also needs to be compatible with the resistance coil, which is 5kVAr, 10kVAr, 20kVAr, 30kVAr or higher.
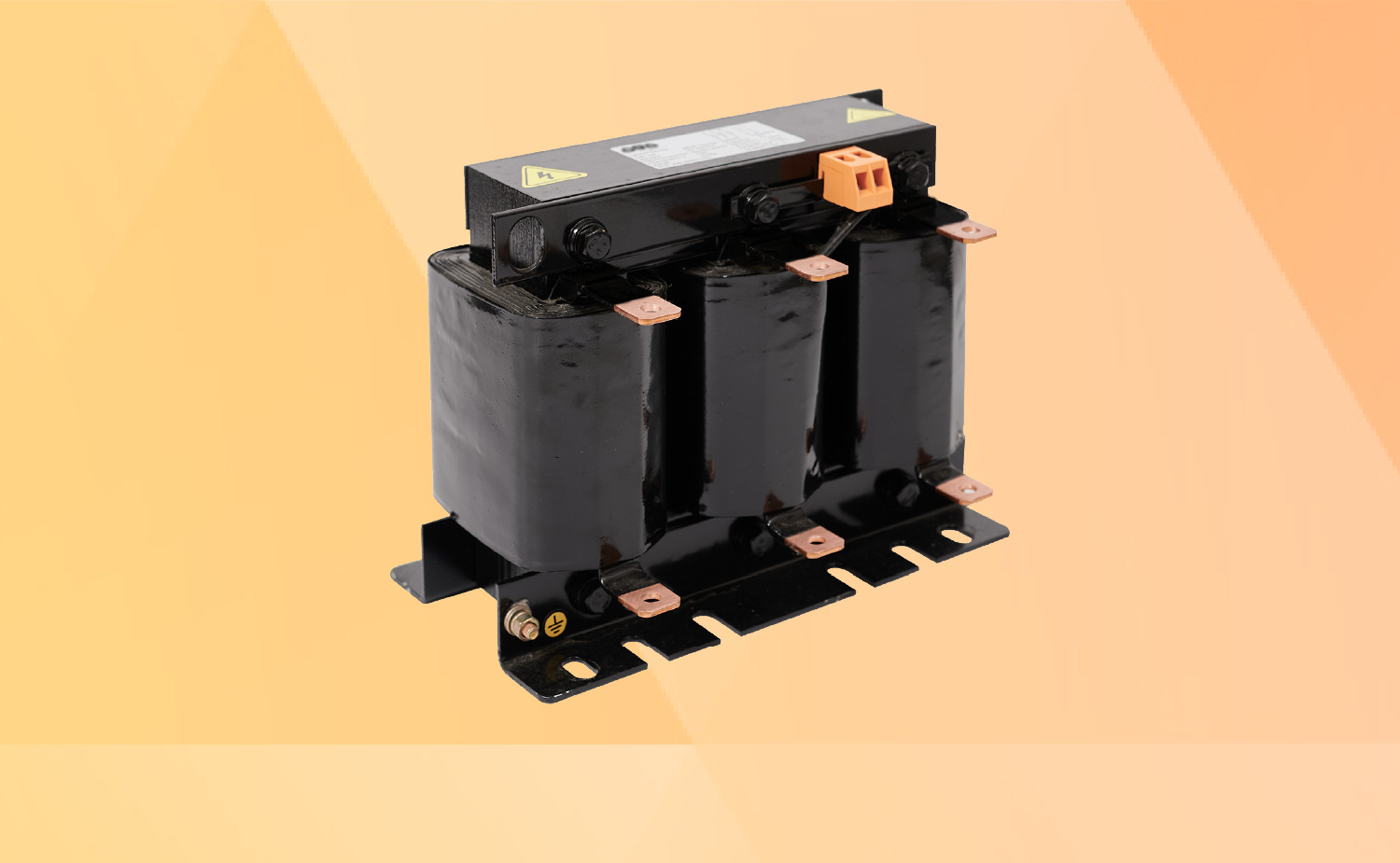

Choosing resistance coils for compensating capacitors from quality electrical equipment brands helps you feel more secure when using and at the same time receive quick warranty and maintenance support. BTB Electric offers electrical resistance coils with a power range from 5kVAr to 30kVAr, 6% - 14% impedance, specially designed with high level of saturation. The product has been applied in low-voltage electrical cabinet systems at factories and medium-voltage electrical cabinets at power companies across Vietnam. Refer to the product at: Resistance Coil for BTB Electric Compensating Capacitors