24-12-2025
Why do electrical systems have 3 phases?
Why only 3-phase power system? why not 6 phase, 9 phase, 12 phase or some other phase?
The number of phases in an electrical system is determined by a number of factors, including efficiency, cost, and ease of use. Three-phase systems are widely used because they offer a good balance between these factors.
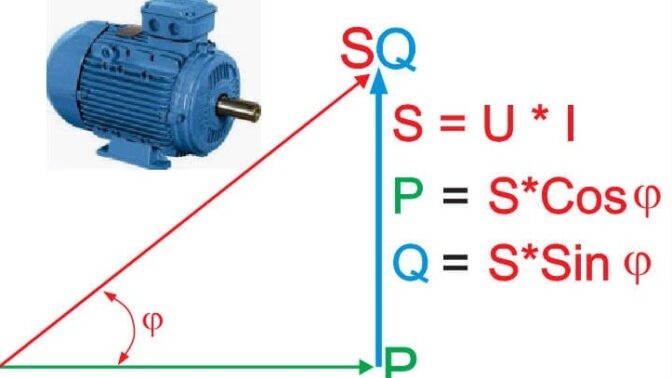
In a three-phase system, energy is transferred by three conductors, each carrying an alternating current that is 120 degrees out of phase with the others. This enables efficient and cost-effective power transmission over long distances. The three-phase system also provides better power factor correction, resulting in lower system losses and improved efficiency.
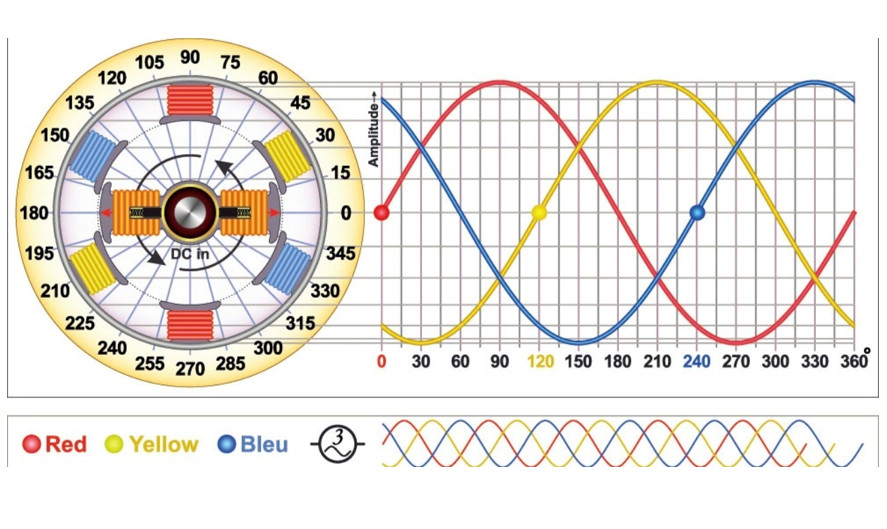
Higher phase numbers, such as 6, 9, or 12, will require additional conductors, making them more complicated and more expensive. Furthermore, they offer no significant benefit over three-phase systems in terms of efficiency or performance. Therefore, 3-phase power system is widely used and preferred in practice. These advantages make it the preferred choice for many applications in the power industry. Here are a few reasons to use a 3-phase system.
Load Balancing: In a three-phase system, the power is evenly divided between the three phases, which helps to balance the load and prevent overloading of any single phase.
Power Quality: Three-phase systems are less susceptible to power quality issues such as voltage sags and harmonic distortions, making them ideal for applications where stable power is required.
Cost-effectiveness: Three-phase systems are cost-effective as they require fewer components compared to higher phase systems, and also provide better system efficiency, reducing the cost of power transmission and distribution.
The law of diminishing returns states that there is a point beyond which increasing the number of phases does not result in a proportional increase in the efficiency of the system. Therefore, using more than three phases would not result in a significant improvement in the efficiency of the system, making the use of three phases the most practical and cost-effective choice
Load balancing: In a three-phase system, the power is divided equally among the three phases, helping to balance the load and prevent overloading in any of the phases.
Power Quality: Three-phase systems are less susceptible to power quality issues such as voltage drop and harmonic distortion, making them ideal for applications that require a stable power supply.
Cost-effective: Three-phase systems are cost-effective because they require fewer components than multi-phase systems, while providing better system efficiency, reducing transmission and distribution costs. power distribution.
The law of diminishing returns states that there is a point beyond which increasing the number of phases does not lead to a proportional increase in the efficiency of the system. Therefore, using more than three phases will not significantly improve system efficiency, making three-phase use the most practical and cost-effective option.