24-12-2025
What is an RCBO? How It Works and Its Practical Applications
An RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection) is a high-performance electrical protection device that responds rapidly to electrical risks. Compared to other circuit breakers such as MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers) and RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers), RCBOs offer additional safety features and enhanced protection capabilities. So, what exactly is an RCBO, how does it work, and how should it be effectively applied in real-world electrical systems? BTB Electric explains below.
Definition and Function of RCBOs
An RCBO is a type of circuit breaker that combines the functions of both an MCB (overload and short-circuit protection) and an RCCB (earth leakage protection). It is designed to protect electrical systems against residual currents, overloads, and short circuits, thereby preventing electric shock and electrical fires.

RCBOs can detect leakage currents and immediately disconnect the circuit, preventing leakage from increasing in magnitude and spreading to connected devices. Essentially, an RCBO integrates the safety features of both RCCBs and MCBs in a single compact device, making it a viable replacement for using separate MCBs and RCCBs in series.
There are two main types of RCBOs:
- Single-phase 1P+N (2-pole) – typically used in residential and commercial systems.
- Three-phase 3P+N (4-pole) – primarily used in industrial power systems.
Leakage current sensitivity levels are commonly rated at 10mA, 30mA, 100mA, 300mA, or higher.
RCBO Construction
Since an RCBO combines the functionalities of an MCB and an RCCB, its internal structure also inherits components from both. The two most critical modules are:
- Arc Divider: Handles overload and short-circuit protection.
- RCD Circuit Board: Detects and responds to earth leakage currents.
Other key components include:
- Thermal Overload Detection: Senses thermal overload conditions.
- Manual Switch: Enables manual operation (ON/OFF).
- RCD Test Button: For testing residual current protection.
- Short Circuit Detection Coil: Identifies and responds to short circuits.
- Toroidal Transformer (RCD Toroid): Measures differential current flow to detect leakage.
Arc Quenching Chamber (Arc Divider)
The arc chamber is composed of metal plates arranged to create a narrow gap that helps quench and cool the arc during circuit interruption. Arc formation typically occurs at the contact points.

There are two main types of arcs:
- Semi-enclosed arc
- Open arc
These types differ in terms of pressure release mechanisms and enclosure structure. Open arcs can handle voltages up to 1,000V and break higher voltages (up to 50kV), whereas semi-enclosed arcs are designed for lower voltage operations.
RCD Circuit Board
The Residual Current Device (RCD) operates by detecting any imbalance between the line and neutral currents passing through a magnetic toroid. If a significant current difference is detected, the magnetic field activates the trip mechanism, disconnecting the circuit.
Key Technical Parameters of RCBOs
- Rated Current (In): The maximum continuous current the RCBO can carry (typically from 6A to 63A).
- Rated Residual Operating Current (IΔn): The minimum earth leakage current required to trip the RCBO (10mA, 30mA, 100mA, 300mA, or 500mA).
- Tripping Time: The response time from detecting leakage to disconnection.
- Number of Poles: Common configurations are 1P+N for single-phase and 3P+N for three-phase. All RCBOs must include a neutral pole for proper operation.
Working Principle of RCBOs
RCBOs operate based on three protection mechanisms:
Earth Leakage Protection
The RCD monitors the balance between live and neutral currents. If a leakage current exists (typically flowing to earth), the imbalance triggers the trip mechanism to open the contacts and disconnect the circuit.
Overload and Short Circuit Protection
Internal contacts are engaged via a latch and spring mechanism. Under overload or short-circuit conditions, magnetic force generated within the coils causes the latch to release, disengaging the contacts and breaking the circuit.
RCBOs integrate both residual current and overcurrent protection, effectively combining the protective roles of MCBs and RCCBs.
Common Types of RCBOs
- 1P+N: For single-phase circuits, connected with one phase conductor and one neutral.
- 3P+N: For three-phase circuits, connected with three phase conductors and one neutral.
Both types share similar installation methods and technical characteristics, with leakage current sensitivity levels ranging from 10mA to 500mA. The primary difference lies in the Applications of RCBOs.
Application of RCBO
RCBOs are ideal for residential, commercial, and industrial electrical protection. By integrating residual current and overcurrent protection into one device, RCBOs reduce the need for separate protective devices, saving both space and installation cost.
They are particularly suitable for:
- Sensitive electrical devices and precision circuits
- High-power appliances (e.g., pumps, grinders, saws, and drills)
- Humid or hazardous environments with increased fire risks
RCBOs are available in different tripping curve types (S, AC, A, F, C, B) tailored for specific loads:
- Type A: For pulsating DC leakage up to 6mA.
- Type F: For devices like dishwashers, air conditioners, and washing machines.
- Type B: For use in 1-phase and 3-phase systems powering welders, elevators, escalators, VFDs, or PV systems.

Devices with leakage up to 300mA can also use RCBOs to prevent fire hazards in demanding environments.
Comparing RCBO with RCCB and MCB

RCBO (Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent protection) and RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) are both circuit breakers capable of detecting residual (leakage) current. In contrast, MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is designed only to protect against overcurrent due to overload or short circuit. RCBOs integrate the functions of both MCB and RCCB into a single unit (modular format). Therefore, RCBOs provide dual protection: Both against electric shock and leakage current like an RCCB and against overload and short circuit like an MCB.
In residential circuits, using an RCBO is a perfect replacement for the MCB and RCCB combination wired in series.
Is RCBO Different from ELCB?
RCBO and ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) are both protective devices that detect leakage current and provide overcurrent protection. However, they differ in both design and principle of operation:
First of all, about the design of product
- RCBO: Modular (MCB-style), integrating MCB and RCCB functions
- ELCB: MCCB-style molded case device
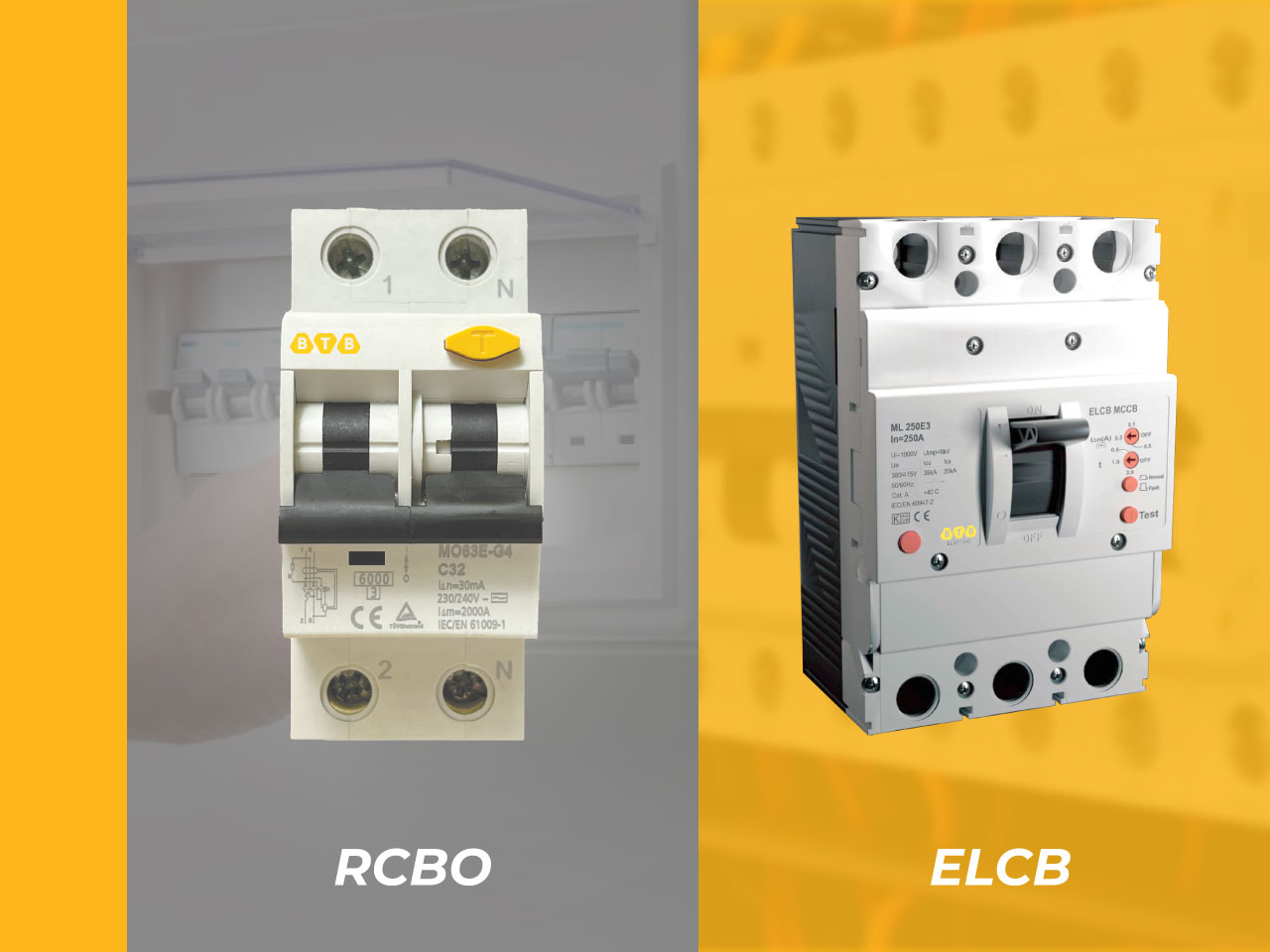

Functionally, both prevent electric shock caused by leakage currents, but:
- ELCB detects current leakage through the earth wire and trips the circuit
- RCBO detects imbalance between phase and neutral conductors and trips when leakage occurs
ELCBs may offer better anti-shock sensitivity, but the choice between ELCB and RCBO depends on the circuit configuration and application.
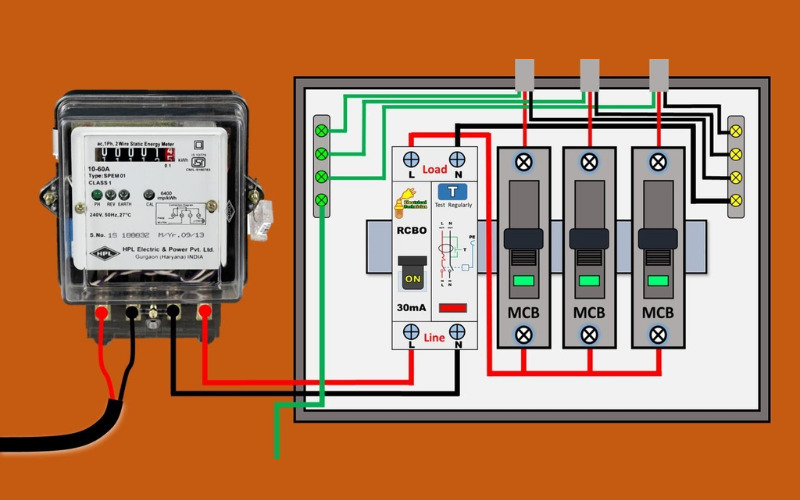
RCBO Installation Guide
There are two typical RCBO installation scenarios. In case, setting up a full installation, you install RCBO similarly to anti electric shock circuit breaker. While adding into an existing system, the RCBO must be connected in series after the main circuit breaker. Before installation, you have to prepare essential tools such as: Voltage tester, Screwdrivers, Wire stripper, Insulated gloves, Electrical pliers and so on.
Installation Steps:
- Step 1: Turn off the main power and notify people nearby. Use a voltage tester to ensure there’s no power before proceeding.
- Step 2: Mount the RCBO onto the electrical panel. Connect the line (input) to the top terminals, and load (output) to the bottom. Notice: Tighten screws securely.
- Step 3: Connect the wiring. Notice: Phase wire (usually red) connecting to Terminal L of RCBO, Neutral wire (usually blue/black) connecting to Terminal N. Never mix up wires or terminals, as this can cause the RCBO to trip immediately or even damage it.
- Step 4: Check wiring direction and grounding. If grounding is present, connect it from the load’s body to the earth system.
How to Test RCBO After Installation
Once installed, you need to ensure that the RCBO is operating safely and reliably. There are two ways to test:
Using the TEST Button
Most RCBOs have a TEST button (marked “T” or “Test”).
- Press the button after power is ON.
- If the RCBO trips immediately → It’s working properly.
- If not → Faulty leakage detection, replacement required

Manufacturers recommend monthly test checks.
Testing with Load (for professionals)
If you have electrical expertise:
- Do not connect the neutral from the load directly to the RCBO.
- Use an intermediate switch with the live wire and measure current using a milliamp meter.
- Power on → If the RCBO trips, it's functioning properly.
- Also calculate expected load current and compare with readings.
Things to Keep in Mind When Choosing RCBOs

- Installation Environment: RCBOs should be installed in dry, ventilated locations, away from direct sunlight or rain. Avoid installing in wet areas (bathroom, kitchen, outdoors) unless using IP-rated protective enclosures.
- Moisture Issues: In humid seasons, condensation may cause unintended tripping. If leakage current is still within safe human limits, consider switching to RCBOs with a higher leakage threshold.
- Routine Testing: Always test the RCBO using the TEST button at least once per month. Avoid conducting manual load tests if you're not trained or lack proper equipment.
Why Choose BTB Electric’s RCBO?

BTB Electric offers high-quality RCBOs certified with the internationally recognized KEMA–KEUR mark.
- Pole configuration: 2P (double pole)
- Rated current: 6A – 63A
- Breaking capacity: up to 6kA
For detailed specifications and product drawings, visit: https://btb-electric.com/rcbo/