24-12-2025
What is Circuit Breaker? Structure, principle of operation and application
Circuit Breaker is the most important equipment in the electrical system, especially home electricity. This is a device that controls the power supply as well as protects the safety of the electrical system. In this article, let's learn with BTB Electric the structure, operating principle and application of Circuit Breaker.
What is a Circuit Breaker?
The main function of Circuit Breaker is to protect the system against overload or short circuit and prevent electrical leakage.
Currently, there are many types of Circuit Breaker with multi-functions, in addition to the usual functions, some types can be anti-shock, lightning or have a reversing function. Circuit Breaker is classified in several ways such as:
- According to the structure: Moulded Case Circuit Breaker and Miniature Circuit Breaker.
- By function: Normal type and type with advanced function.
- According to the parameters: By the number of phases (1 – 3 phases) and by the number of poles (1 – 4 poles).
- According to the short-circuit cut-off line: Depends on the purpose of use for residential electricity, production power, transmission power or special purposes.
Functions of Circuit Breaker
The basic function of Circuit Breaker is to protect electrical circuits against electrical system risks including.
- Overload Protection: When the current exceeds the safety rating, the Circuit Breaker will automatically shut off the circuit to prevent the overload current, preventing the device from heating or exploding. This function is available on the MCB, MCCB, RCBO and ELCB series.
- Short Circuit Protection: When the current rises suddenly, causing a short circuit, the Circuit Breaker will shut itself off to prevent the device or line from exploding. This function is available on the Circuit Breaker: MCB, MCCB, RCBO and some ELCB series.
- Anti-shock, anti-leakage: When detecting a current difference in the AC circuit (with leakage current), Circuit Breaker will quickly interrupt the circuit to prevent the leakage current from spreading, the risk of electric shock to the user. This function is available on anti-leaked current Circuit Breaker lines such as RCBO, RCCB and ELCB.
- Anti-phase loss, lightning protection, overvoltage resistance: Functions on some specific Circuit Breaker lines.
Circuit Breaker detects faults in current through parameters such as amperage (A), short-circuit current (kA) or leakage current (mA). As soon as it detects that the current encounters one of the above phenomena with a value exceeding the rated value, the Circuit Breaker will immediately shut down to prevent the current from flowing through, protecting the safety of the rear load equipment.
Structure of Circuit Breaker
Common structural features of Circuit Breaker include: contacts, Arc arrester, actuator and tripping mechanism.
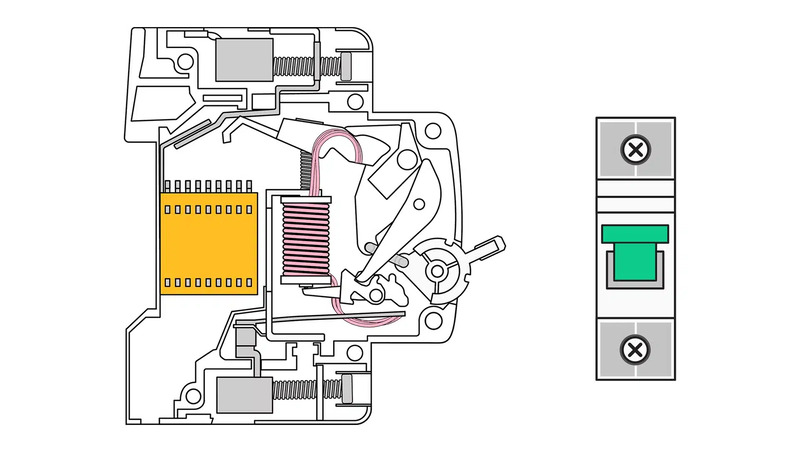
Contact
The contact in the Circuit Breaker performs a circuit closure and circuit breaker. Depending on the type of Circuit Breaker, the contact can be divided into 2 types (dynamic and static). The static contact is connected to the external wire leading into the Circuit Breaker. The dynamic contact is attached to an electromagnet and movable.
Arc arrester
In order to handle electric arc arresters in all operating conditions of the power system, two types of arc arrester equipment are commonly used: semi-sealed type and open type. The semi-sealed type is arranged inside the sealed case of the CB and has an air outlet hole. This type has a current cut-off limit that does not exceed 50KA. The open type is used when the cut-off current limit is greater than 50KA or the voltage is greater than 1000V (high voltage).
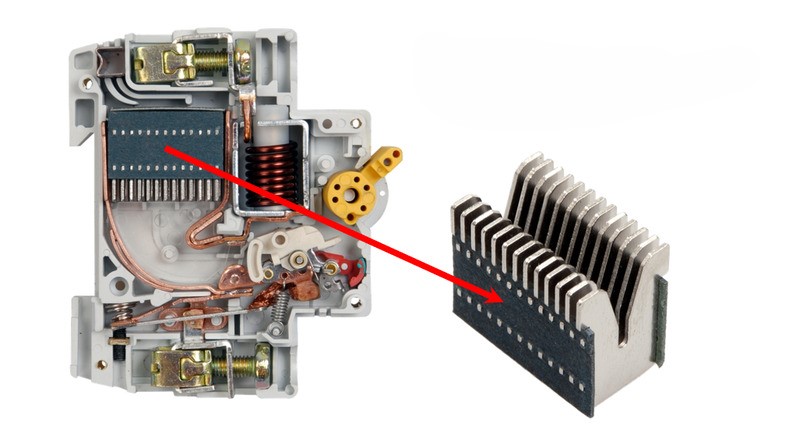
In the electric arc arrester chamber at Circuit Breaker, steel plates are used arranged in a network to divide the arc into several short sections, which helps to extinguish the arc effectively.
Cut-off drive mechanism
There are 2 ways to control the cutting drive mechanism, either by hand or by electromechanical (electromagnetic, electric motor):
- Manual cut-off drive: used for Circuit Breaker with rated current below 125A, usually found in residential and commercial electrical systems.
- Electromechanical cutting drive: used for Circuit Breaker with high rated current from 125A to 1000A, widely used in industry.
Tripping mechanism
The tripping mechanism is the signal transmission unit in the Circuit Breaker, acting on the circuit when it detects signs of overload or short circuit or voltage drop so that the Circuit Breaker automatically cuts off the power. There are two common types of tripping mechanism, electromagnetic systems and thermal relays.
- The solenoid type hook consists of a coil that is connected in series to the main circuit, which has a large cross-section to withstand current and few winding loops. When the current exceeds the allowable value, the magnetic force will pull the armature in and the hook will hit the free-falling joint, causing the contact of the CB to open. By adjusting the resistance of the spring through the screw, the current value can be adjusted instantly. To keep the time in the overload protection of the solenoid-type hook, a time-holding mechanism is added.
- Thermal relay type hooks have a simpler structure, similar to thermal relays with a heat-generating element connected next to the main circuit. An expanded double metal plate will cause the joint to fall freely, opening the contact of the CB when overload occurs. The disadvantage of this type is the large thermal delay, so it cannot quickly interrupt the abnormal current when there is a short circuit problem, and therefore can only protect against overload current.
Normally in Circuit Breaker up to 600A arrange both solenoid hooks and relay hooks. In the case of the voltage drop tripping mechanism, the electromagnetic type is used, which is a coil caught in parallel with the main circuit, with few loops and a small wire cross-section.
Important specifications on Circuit Breaker

Here are the specifications of Circuit Breaker:
- Ui: Rated working voltage.
- Ue: Rated insulation voltage.
- ln: It is the rated current. For example in MCCB 3P 100A 25kA, In=100A. The main rated current is the overload protection threshold of Circuit Breaker. When the current exceeds the rating, the Circuit Breaker will TRIP.
- Ir: The operating current is adjustable within the allowable range of the Circuit Breaker. For example, a 100A current regulated Circuit Breaker is adjustable to 100A. For current regulated Circuit Breakers, the operating current is the Circuit Breaker's acting threshold.
- Icu: The short-circuit cut-off current is the contact's maximum current tolerance for 1 second.
- Icw: Short-circuit current tolerance per 1 unit of time.
- Ics: The actual ability to cut when a problem occurs on the equipment, depends on each manufacturer due to different manufacturing technology. For example, the same manufacturer but has 2 types of MCCB: Ics = 50% Icu and Ics = 100% Icu.
- IΔn: Ability to withstand electrical leakage current, available in mA.
- AT – Ampere Trip: It is the impact current.
- AF – Ampere Frame: It is the frame current. For example, NF250 2P 100A and NF250 2P 200A both have AF=250A, but one will impact when the current exceeds AT=200A, the other will impact when the current exceeds AT=100A.
- Characteristic curve: It is the protection characteristic curve of the CB (the selective curve of the CB) that helps to decide where the CB is selected in the electrical system.
- Mechanical/electrical endurance: The number of permissible mechanical switches exceeds the allowable number of electrical switches.
Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
The main function of the Circuit Breaker is to disconnect the circuit when a fault is detected in the electrical system. If a sudden change in the current flowing through the circuit through the contact occurs, the magnetic field created on the spring (the voltage is too low) will be decreased or the spring will overheat (the voltage is too high), causing the contacts to open and the current to be interrupted.
For circuit breakers used for household electrical appliances, users will have to manually reset them to control the devices to operate again. Circuit breakers for electrical systems with higher cutting currents often have an electromagnetic control mechanism.
After the short circuit has occurred for a while, the springs in the circuit breaker will return to normal so that all contacts can connect to each other again, allowing the current to continue to go through .
Circuit Breaker’s classification
When classifying by the number of phases and poles, Circuit Breaker has types: 1 phase 1 pole, 1 phase 2 poles, 2 phase 2 poles, 3 phase 3 poles, 3 phase 4 poles.
When classifying by amperage (In), Circuit Breakers are divided by:
- Low Print Level: 1A, 2A, 3A, 6A,.... 125A
- Average Printing Level: 160A, 250A, 320A, 400A,... 800A
- High Printing Level: 1000A, 1250A, 1600A, 2500A,...
Circuit Breaker is divided into many types for use for 1-phase electricity and 3-phase electricity. The most popular are the MCB, MCCB, RCCB, RCBO and ELCB Circuit Breaker series. With each of the above types, there are many levels of rated lines, many different pole numbers and features.
Miniature Circuit Breaker

MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) is a small size Circuit Breaker series, used for 220V and 380V power networks. MCB has a low rated current, from 125A or less, suitable for installation for home power systems or small and medium-power electrical equipment. The function of MCB is to resist electrical overload and resist short circuit. MCB is very popular in residential houses, apartment buildings, offices, business stores, warehouses, hotels, hospitals, schools,...
Moulded Case Circuit Breaker
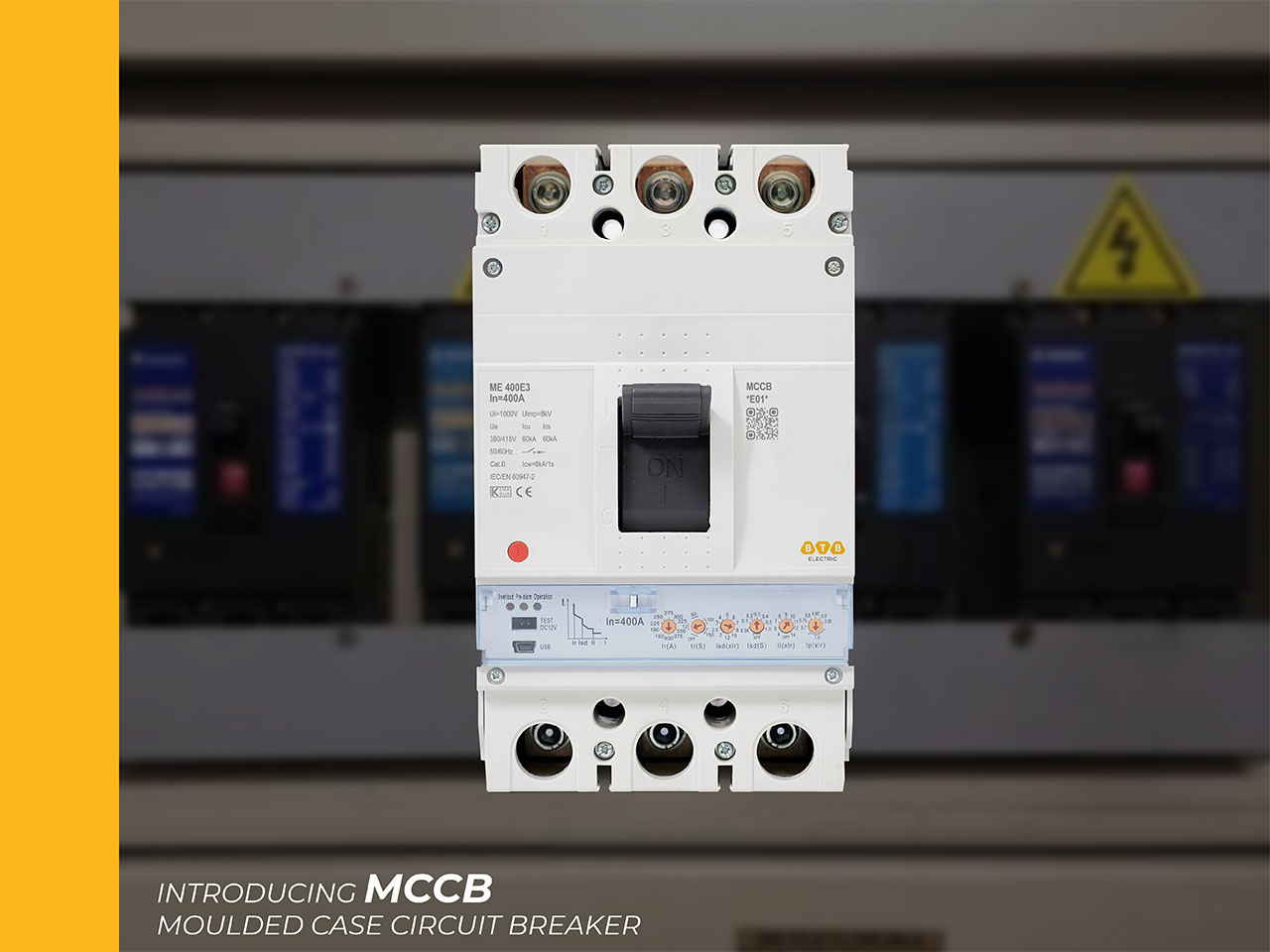

MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) is a large-size block Circuit Breaker, used for 380V power networks, carrying a rated current from 6A to 2500A. MCCB protects the electrical network from overload and short circuit. The special feature of the MCCB is that it can be controlled remotely as well as the rated line break level can be adjusted. MCCB is an indispensable switchgear in industrial electrical cabinets in power plants, manufacturing plants, warehouses, seaports, airports,...
Residual Current Circuit Breaker

RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is a series of specialized Circuit Breaker anti-electric shock, used for both 220V and 380V power networks. This type of Circuit Breaker has a variety of rated currents from 16A to hundreds of amperes. RCCB is often installed in addition to electrical systems that do not have anti-shock features, placed in series with an anti-overload, short-circuit Circuit Breaker. Along with that, the leakage current levels of RCCB range from 10mA to 500mA.
Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection

RCBO (Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overcurrent Protection) is an Circuit Breaker series that combines shock resistance and overload and short-circuit resistance. This type of Circuit Breaker has a variety of leakage current levels and short-circuit cut-off current levels. RCBO is mainly used for 220V circuits, replacing MCB and RCCB simultaneously. In addition, RCBO can be applied to 380V industrial circuits
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker

ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is a block-type earth leakage circuit breaker with overload resistance. This device is often used to prevent electrical leakage in sensitive, high-humidity environments. In some cases, ELCB can replace MCCB – RCCB or install some specialized electrical equipment.
Application of Circuit Breaker
Circuit Breaker is an important electrical device, present in any low-voltage power system, from residential, commercial to industrial. The uses of Circuit Breaker include:
- Control and protect electrical circuits, ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Timely circuit breaker when detecting electrical problems such as overload, phase loss, short circuit,...
- Some Circuit Breakers have the ability to protect systems and people from electrical leaks, lightning strikes, floods, and fires,...
- Limit damage such as heat, fire and explosion for load equipment.
Application in industrial power
In industry, MCCB is mainly used, besides specialized switchgear. Equipped with an arc arrester, the MCCB series can interrupt the current up to thousands of Amps. If a MCB is used, choose a 3-phase type with a 10kA short-circuit cut-off current.

The majority of electrical equipment in industry is 3-phase electrical equipment. Although the system uses a neutral wire, because problems on the neutral wire are rare, only 3-pole Circuit Breaker type is usually used to save costs. For total Circuit Breaker positions, it is necessary to choose one with a high short-circuit cut-off current to ensure safety. As for the branch Circuit Breakers used for the device, it is possible to choose the type with medium cutting current.
Application in civil power
The majority of electrical appliances in the home are 1-phase electrical appliances. In this case, it is common to use a 1-phase MCB to insert into the phase wire (fire wire), while the neutral wire (mass wire) does not need to go through the MCB. On the other hand, because there is no arc arrester, the Circuit Breaker MCB can only cut off the current below 100A.

Normally, people will choose MCB with a short-circuit cut-off current of 6kA or 4.5kA to save costs. For some households with large electricity consumption and using 3-phase electricity, it is recommended to choose a total Circuit Breaker with a medium short-circuit cut-off current to ensure the safety of the power system and higher durability.
The use of high-power electrical appliances is becoming more and more common. To ensure the safety of the electrical system, devices with a high operating power of 1000W should be protected with their own anti-shock Circuit Breakers, such as heaters, air conditioners, induction cooktops,...
Some questions
Question 1: Is there a difference between choosing a 1-phase Circuit Breaker and a 3-phase Circuit Breaker?
Answer: The 1-phase Circuit Breaker uses a 220V circuit for residential electricity, the 3-phase Circuit Breaker uses a 380V circuit for industrial electricity. Thus, it is necessary to understand the electrical system used to choose 1 of the 2 types of Circuit Breakers above.
Question 2: How to choose the suitable Circuit Breaker capacity?
Answer: When you calculate the capacity of the devices used in the system, you will get the total capacity. Choose an Circuit Breaker capacity that is 30-50% higher than the total capacity to minimize the risk of overvoltage or sudden increase in capacity utilization.
Question 3: What is the function of Circuit Breaker in the indoor power network?
Answer: Circuit Breaker automatically switches the circuit when there is an overload, short circuit, or electrical leakage.
Question 4: Which brand of Circuit Breaker should I use?
Answer: There are many quality Circuit Breaker manufacturers to choose from. For industrial power systems, priority is given to using Circuit Breaker from ABB, BTB Electric, Mitsubishi, Schneider,... For residential electrical systems, priority is given to using Circuit Breaker from LS, Panasonic,...
Above is a summary of information about Circuit Breaker, typical structure, principle of operation and application in life of this extremely important electrical device. For more information about Circuit Breaker, please continue to follow on the https://btb-electric.com/ website.