24-12-2025
What is a Thermal Relay? Structure and principle of operation of thermal relay
Thermal relays or thermal relays are important electrical protection devices in any electrical system thanks to their ability to resist temperature overloads. Let's follow the sharing from BTB Electric through the following article to better understand the structure, working principle, function and application of thermal protection relays.
What is a Thermal Relay?
Thermal relay is an electrical device used to protect an electrical device or system against temperature overload. The task of the thermal relay is to monitor the system temperature and cut off the power in time when it exceeds the specified limit.
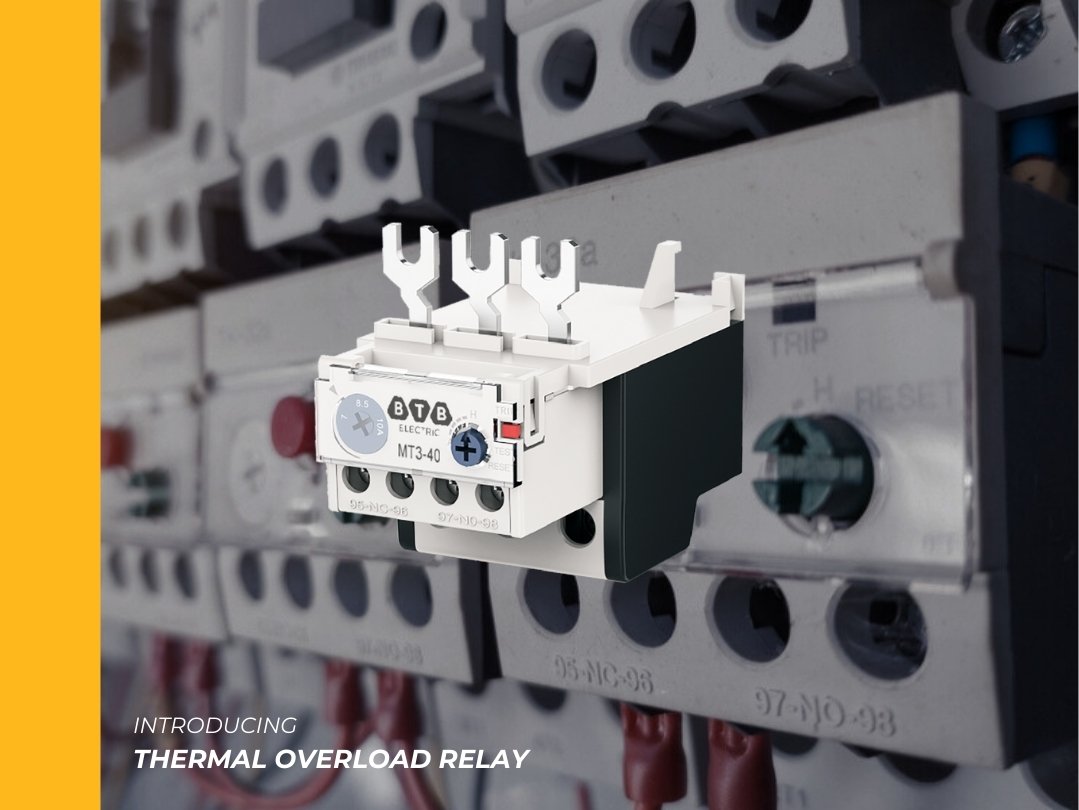
Short-term electrical overload can still be safe for electrical equipment. However, if this situation lasts for a long time, it will cause losses such as line melting, equipment rust,.. Therefore, the overheating protection feature of the temperature relay is very necessary. This capability helps minimize damage to power lines and equipment, and prevents the risk of fire, ensuring user safety.

The temperature relay was invented in 1835 by Joseph Henry, an American electrical scientist. Based on the phenomenon that small electromagnets can control larger ones, he believes that relays are capable of controlling electrical equipment over long distances.
Function of Thermal Relay
Thermal relays are used in large power systems such as industrial plants, air conditioning systems, civil power systems. When the system temperature rises beyond the limit, this type of relay will detect and disconnect the input power. This action helps the system to stop operation and prevent risks due to temperature overloads.
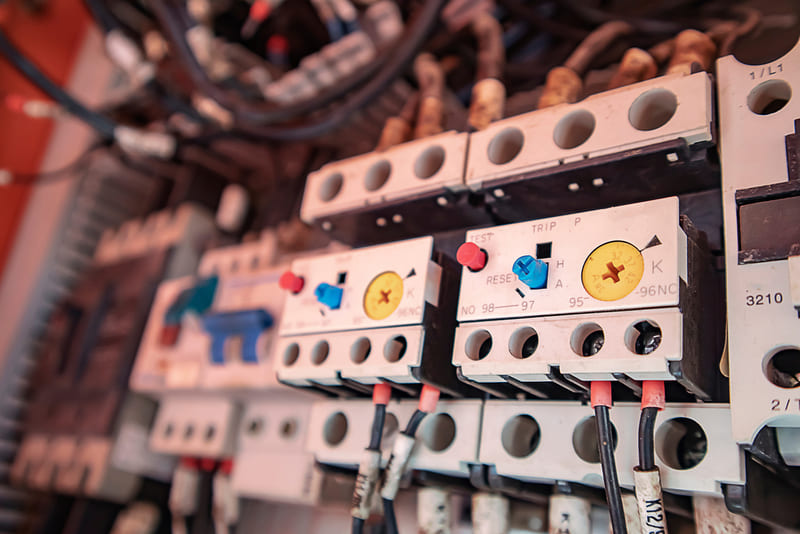
The heat relay also has the function of reducing the risk of fire. When the system is overheated, it is easy to melt and explode, causing fire. When this risk is detected, the relay will cut off the power to prevent the temperature from rising, limiting fire and damage later.
Structure of Thermal Relay
The structure of a thermal relay consists of 3 main components: a thermal sensor, a signal converter and a starter.
Thermal Sensor: Arranged close to the protected device face, it is responsible for measuring the temperature of the material. This component consists of 2 types: bimetallic strip and thermoelectric type. The bimetallic rod consists of 2 metal rods attached to each other. When the temperature changes, the bimetal rod twists, activating the thermal relay motor and shutting off the circuit. A thermoelectric sensor is a pair of wires of different materials placed next to each other. When the temperature changes, a potential difference between the 2 wires appears that triggers the thermal relay.
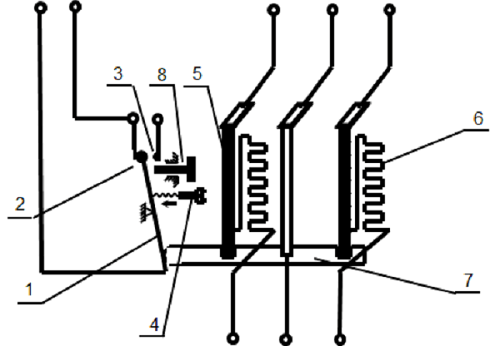
Signal converter: Usually an electronic circuit in a relay. The unit receives the signal from the thermal sensor and converts it into an electrical signal. Based on the thermal signal obtained, this unit will measure whether the starter needs to be activated.
Starter: It is the part that triggers the power shut-off when there is a temperature signal that exceeds the allowable threshold. After a signal is obtained from the signal converter, the starter will command when to cut off the power to protect the system.
The components included in thermal relays usually have components: levers, NC normally closed contacts, NO normally open contacts, bimetal rods, burners, levers, reset buttons,... And when observing the outside of the thermal relay, here are some important details you need to know:
- Connection terminals: Symbol L1, L2, L3 to attach to the contactor with contacts T1, T2, T3 or attach to some other electrical equipment.
- Pin COM: Where to connect the standby power cord and connect to 1 of the 2 NO or NC pins, depending on the status of the thermal relay.
- NC Legs: Legs are usually closed. When the thermal relay is in the OFF state, this pin will connect to the COM pin.
- Leg NO: Legs are usually open. When the relay is ON, this pin will connect to the COM pin
- Amplifier Range Setting: Is 1 knob to set the rated current of the device.
- Reset Button: Button to reset the operation of the relay or clear the fault.
- Test Button: Used to check the control wire of the thermal relay.
Specifications of Thermal Relay
The important specifications of thermal relays are:
- Thermal protection strip: The working current strip of the thermal relay.
- Number of poles: 3P, 1P.
- Sub-contacts: Number of normally closed (NC) and normally open (NO) sub-contacts
- Operating Frequency: Mainly 50/60Hz
- Contactor compatibility: Each type of thermal relay will be suitable for installation into a specific contactor strip, compatible with current and frame size.
- Ue, Ui, Uimp: Parameters of operating voltage, insulation, and rated pulse resistance.
Working Principle of Thermal Relay
The working principle of the thermal relay is based on the thermal response of the thermal sensor (metal rod pair or conductor pair). When the overload current will generate heat gradually, until the comparison threshold of the thermal sensor is exceeded, the relay sends a signal to the starter to interrupt the circuit.
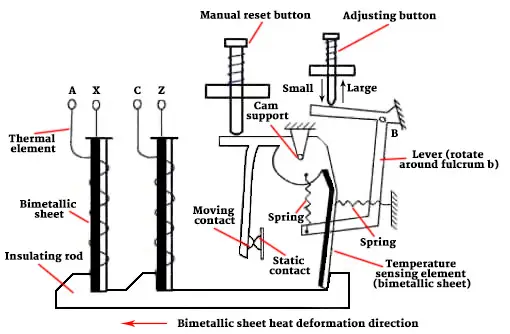
If the thermal sensor is a double metal rod, when the temperature is too high, it will cause the metal rod to twist towards the metal side with a lower coefficient of expansion. If the thermal sensor is a pair of wires, the relay will detect a current difference running through the 2 wires when it is overloaded.
There are two forms of reset of the thermal relay: automatic and manual. The selection of the thermal relay will be based on how the reset screw is adjusted. In fact, the relay is attached to the motor, and only when the relay is reset manually can the motor start.
Common types of thermal relays
When classified by voltage, thermal relays include 2 types: 1-phase and 3-phase:
- 1 Phase Relay: Used in 220V home electrical systems to protect electrical systems and home electrical appliances such as lights, fans, refrigerators,...
- 3-phase relay: Used for 380V industrial power system to monitor the operation of the whole system and protect high-power electrical equipment.

In addition to the two common thermal relay lines classified by voltage, there are also some specialized relay lines for electrical equipment such as:
- Rice cooker heat relay: Automatically expands to cut off the power to the rice cooker when there is a sign of overload or rice cooking.
- Water Pump Thermal Relay: Automatically expands when the water pump is overloaded or the pump is waterless to cut off the power and avoid shorting the pump.
- Iron Thermal Relay: When the temperature is too high, this unit will bend to disconnect the circuit and straighten out when the temperature drops to heat the iron.
- Heater Heat Relay: Prevents the water in the heater from exceeding the limit by temporarily interrupting the current to the water heater.
Application of Thermal Relay
Thermal relays are installed with contactors, widely applied in industries such as automation, manufacturing, mining, construction, agriculture, power transmission,... The main use of the device is to monitor the operation of the electrical system, identify thermal overload locations and provide appropriate circuit breaker plans to limit damage.

In addition, heat relays are also used in civil electrical systems for the purpose of thermal protection for electrical equipment such as pumps, water heaters, rice cookers,...
Notes when choosing the right thermal relay for the circuit
A few factors to keep in mind when choosing a thermal relay:
- Determine the overload current of the device: The overload current level of the equipment to be protected should be equal to and higher than the circuit breaker level of the relay.
- Determine the overload temperature value: Select the value according to the operating power system and the overload current level. If the temperature is selected too low, it will cause the thermal relay to jump continuously. In case of choosing too high a temperature, it is easy to damage the device without the relay jumping.
- Choose the method of thermal relay operation: There are 2 types: instantaneous interrupt and delayed interrupt. Some relay series have an additional phase loss protection.
- Choose the type of power voltage: Choose 3-phase power or 1-phase power depending on the reality.
- Choose the type of thermal relay: There are common types of relays for multiple devices or specialized relays for 1 type of equipment. There is also a line of thermal relays that are only compatible with certain types of contactors.

The above information from BTB Electric has helped you better understand thermal relays – a type of overload protection device that is widely used today. You can learn more about this device through the BTB Electric thermal relay product.
Some questions about thermal relays
Question 1: Can the thermal relay switch the circuit?
Answer: Thermal relays are capable of switching electrical circuits, but not on the main motive circuit but on the control circuit of the contactor with a small current. The circuit breaker is performed when the thermal relay detects a thermal overload on the circuit.
Question 2: Why are thermal relays often installed together with contactors?
Answer: Thermal relays are usually installed with contactors to form magnetic starters with the function of switching and protecting the motor, which helps to better control and control the motor, limit overload on the circuit and increase motor life.
Question 3: Why do thermal relays have a current adjustment strip instead of a fixed one?
Answer: The thermal relay has a current adjustment strip to be compatible with a wide range of motors, accurately adjusting the current according to actual conditions and optimizing the current protection threshold.
Question 4: What problems can damage the thermal relay?
Answer: A number of problems can damage thermal relays: current overload, short circuits, unstable voltages, harsh installation environments, wear and tear on relay components, improper installation, and electric arcing when shutting down.